Back
Poster Session C
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
Session: (1440–1485) SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster II: Manifestations
1462: Exploring the Potential of Urine: Serum Fractional Excretion Ratios as Disease Biomarkers in Active Lupus Nephritis
Sunday, November 13, 2022
1:00 PM – 3:00 PM Eastern Time
Location: Virtual Poster Hall
- SS
Samar Soliman, MD, PhD
Faculty of Medicine, Minia university
Minya, Egypt
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Samar Soliman1, Samantha Stanley2, Kamala Vanarsa2, Faten Ismail3, Chi Chiu Mok4 and Chandra mohan5, 1Rheumatology Department, Faculty of Medicine, Minia university, Minya, Egypt, 2Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Houston, Houston, TX, 3Department of Rheumatology, Faculty of Medicine, Minia University, Minia, Egypt, 4Tuen Mun Hospital, Hong Kong, China, 5University of Houston, Houston, TX
Background/Purpose: The goal of this exploratory study is to determine if urine:serum fractional excretion ratios can outperform the corresponding urinary biomarker proteins in identifying active renal disease in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
Methods: Ninety-six adult SLE patients and twenty-five healthy controls were examined for serum and urine levels of 8 protein markers, namely ALCAM, Calpastatin, hemopexin, Peroxiredoxin 6 (PRX6), Platelet factor 4 (PF4), properdin, TFPI and VCAM-1, by ELISA. Fractional excretion of analyzed biomarkers was calculated after normalizing both the urine and serum biomarker levels against creatinine using the following equation, the same way fractional excretion of sodium is calculated: Fractional Excretion (FE)= (Urine biomarker/urine Cr) ÷ (Serum biomarker/serum Cr).
SLE disease activity was assessed using SLEDAI-2K. Renal activity was assessed using the renal domain scores of SLEDAI (range 0–16; 0 = inactive LN). At enrollment, patients were categorized into 3 groups; active renal SLE (LN, patients with renal SLEDAI score ≥ 4), active non-renal SLE (patients with total clinical SLEDAI ≥1, but renal SLEDAI=0) and inactive SLE (patients with total clinical SLEDAI = 0, asymptomatic with no findings of organ activity, subclinical hypocomplementemia and/or elevated autoantibodies allowed). The active renal group's renal histopathologic features were analyzed using a kidney biopsy.
Results: The FE ratios of all 8 proteins interrogated outperformed conventional disease activity markers such as anti-dsDNA, C3 and C4 in identifying renal disease activity. All FE values were superior to the corresponding urine biomarkers levels in differentiating LN activity. Urine levels of all biomarker proteins assayed were highest among active LN patients, however, the serum levels of the assayed proteins from the same patients were not significantly different between the SLE patient groups among levels of sALCAM, sHPX, sPRX6 and sProperdin. PF4FE correlated significantly with all conventional disease activity parameters including SLEDAI, renal SLEDAI, PGA, complement C3, C4 and anti-dsDNA. Renal SLEDAI scores exhibited the best correlation coefficients with FE ratios of the assayed biomarkers, showing strong significant correlation with properdinFE (Rho 0.79, P< 0.0001), followed by ALCAMFE (Rho 0.64, P< 0.0001), CalpastatinFE(Rho 0.64, P< 0.001), and PRX6FE (Rho 0.64, P 0.01). PF4FE, TFPIFE and VCAM-1FE values showed "good" significant correlations with renal SLEDAI (Rho 0.58, 0.58, 0.49 respectively). ALCAMFE, PF4FE and properdinFE ratios exhibited the highest accuracy (AUC >0.9) in distinguishing active LN from inactive SLE. Four of the FE ratios exhibited perfect sensitivity (Calpastatin, PRDX6, PF4 and properdin), while ALCAMFE, PF4FE and properdinFE exhibited the highest specificity values for active LN.
Conclusion: With most of the tested proteins, the urine:serum fractional excretion ratios outperformed corresponding urine protein measurements in identifying active renal involvement in SLE. Hence, this novel class of biomarkers in SLE ought to be systemically evaluated in larger independent cohorts for their diagnostic utility in LN assessment.
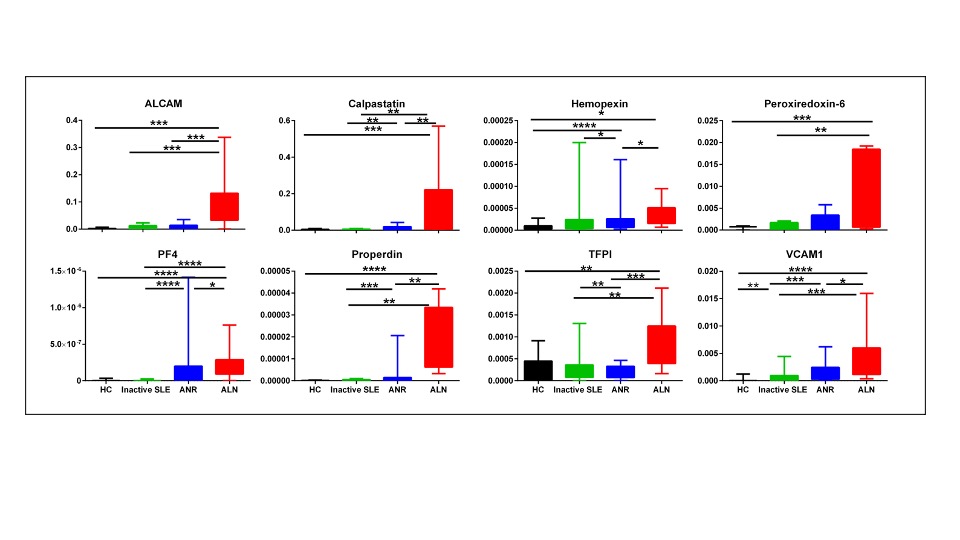 Fractional Excretion ratios of eight protein biomarkers in SLE patients and controls. Fractional excretion (FE) ratios of all 8 biomarker proteins were calculated by dividing the urine biomarker levels by the corresponding serum biomarker levels, after normalizing both against urine or serum creatinine, respectively. The Y axes show the values of the fractional excretion ratios of studied biomarkers as well as their SE (error bars), while the X axes display the 4 groups interrogated (25 healthy controls; 32 inactive SLE; 31 active non-renal disease; 33 active renal disease). * = P < 0.05, ** = P < 0.01, *** = P < 0.001, **** = P < 0.0001.
Fractional Excretion ratios of eight protein biomarkers in SLE patients and controls. Fractional excretion (FE) ratios of all 8 biomarker proteins were calculated by dividing the urine biomarker levels by the corresponding serum biomarker levels, after normalizing both against urine or serum creatinine, respectively. The Y axes show the values of the fractional excretion ratios of studied biomarkers as well as their SE (error bars), while the X axes display the 4 groups interrogated (25 healthy controls; 32 inactive SLE; 31 active non-renal disease; 33 active renal disease). * = P < 0.05, ** = P < 0.01, *** = P < 0.001, **** = P < 0.0001.
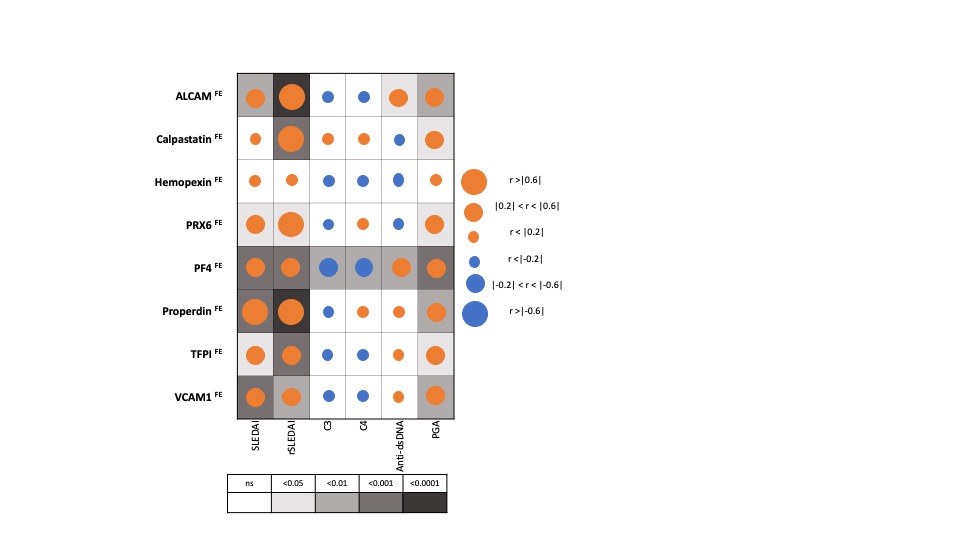 Correlation of Fractional Excretion (FE) ratios of eight protein biomarkers with conventional disease activity measures in SLE. The derived FE ratios of the eight interrogated biomarkers were examined for their correlation with SLEDAI, renal-SLEDAI, C3, C4, anti-dsDNA and Physician Global Assessment (PGA) values. Positive and negative correlations are denoted by orange and blue circles respectively, while statistical significance is denoted using grey-scale boxes. Overall, the urine biomarker fractional excretion ratios correlate best with renal-SLEDAI in LN.
Correlation of Fractional Excretion (FE) ratios of eight protein biomarkers with conventional disease activity measures in SLE. The derived FE ratios of the eight interrogated biomarkers were examined for their correlation with SLEDAI, renal-SLEDAI, C3, C4, anti-dsDNA and Physician Global Assessment (PGA) values. Positive and negative correlations are denoted by orange and blue circles respectively, while statistical significance is denoted using grey-scale boxes. Overall, the urine biomarker fractional excretion ratios correlate best with renal-SLEDAI in LN.
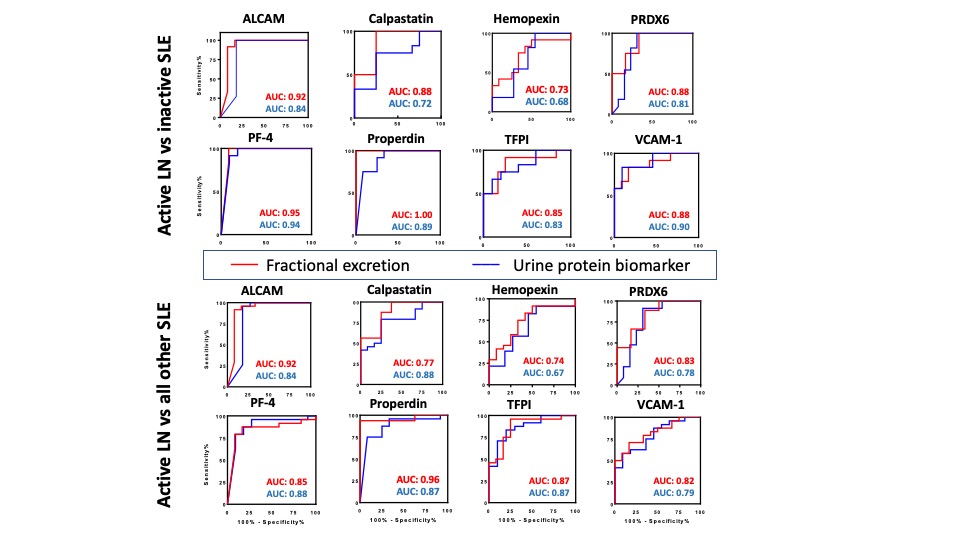 Comparing the diagnostic potential of FE ratios and their corresponding urine biomarkers in identifying active LN. Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curves were generated for the 8 urine protein markers (blue line) and their corresponding FE ratios (red line) in differentiating active lupus nephritis from inactive SLE (top) and active lupus nephritis from all other SLE patients (active non-renal and inactive SLE) (bottom)
Comparing the diagnostic potential of FE ratios and their corresponding urine biomarkers in identifying active LN. Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curves were generated for the 8 urine protein markers (blue line) and their corresponding FE ratios (red line) in differentiating active lupus nephritis from inactive SLE (top) and active lupus nephritis from all other SLE patients (active non-renal and inactive SLE) (bottom)
Disclosures: S. Soliman, None; S. Stanley, None; K. Vanarsa, None; F. Ismail, None; C. Mok, None; C. mohan, None.
Background/Purpose: The goal of this exploratory study is to determine if urine:serum fractional excretion ratios can outperform the corresponding urinary biomarker proteins in identifying active renal disease in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
Methods: Ninety-six adult SLE patients and twenty-five healthy controls were examined for serum and urine levels of 8 protein markers, namely ALCAM, Calpastatin, hemopexin, Peroxiredoxin 6 (PRX6), Platelet factor 4 (PF4), properdin, TFPI and VCAM-1, by ELISA. Fractional excretion of analyzed biomarkers was calculated after normalizing both the urine and serum biomarker levels against creatinine using the following equation, the same way fractional excretion of sodium is calculated: Fractional Excretion (FE)= (Urine biomarker/urine Cr) ÷ (Serum biomarker/serum Cr).
SLE disease activity was assessed using SLEDAI-2K. Renal activity was assessed using the renal domain scores of SLEDAI (range 0–16; 0 = inactive LN). At enrollment, patients were categorized into 3 groups; active renal SLE (LN, patients with renal SLEDAI score ≥ 4), active non-renal SLE (patients with total clinical SLEDAI ≥1, but renal SLEDAI=0) and inactive SLE (patients with total clinical SLEDAI = 0, asymptomatic with no findings of organ activity, subclinical hypocomplementemia and/or elevated autoantibodies allowed). The active renal group's renal histopathologic features were analyzed using a kidney biopsy.
Results: The FE ratios of all 8 proteins interrogated outperformed conventional disease activity markers such as anti-dsDNA, C3 and C4 in identifying renal disease activity. All FE values were superior to the corresponding urine biomarkers levels in differentiating LN activity. Urine levels of all biomarker proteins assayed were highest among active LN patients, however, the serum levels of the assayed proteins from the same patients were not significantly different between the SLE patient groups among levels of sALCAM, sHPX, sPRX6 and sProperdin. PF4FE correlated significantly with all conventional disease activity parameters including SLEDAI, renal SLEDAI, PGA, complement C3, C4 and anti-dsDNA. Renal SLEDAI scores exhibited the best correlation coefficients with FE ratios of the assayed biomarkers, showing strong significant correlation with properdinFE (Rho 0.79, P< 0.0001), followed by ALCAMFE (Rho 0.64, P< 0.0001), CalpastatinFE(Rho 0.64, P< 0.001), and PRX6FE (Rho 0.64, P 0.01). PF4FE, TFPIFE and VCAM-1FE values showed "good" significant correlations with renal SLEDAI (Rho 0.58, 0.58, 0.49 respectively). ALCAMFE, PF4FE and properdinFE ratios exhibited the highest accuracy (AUC >0.9) in distinguishing active LN from inactive SLE. Four of the FE ratios exhibited perfect sensitivity (Calpastatin, PRDX6, PF4 and properdin), while ALCAMFE, PF4FE and properdinFE exhibited the highest specificity values for active LN.
Conclusion: With most of the tested proteins, the urine:serum fractional excretion ratios outperformed corresponding urine protein measurements in identifying active renal involvement in SLE. Hence, this novel class of biomarkers in SLE ought to be systemically evaluated in larger independent cohorts for their diagnostic utility in LN assessment.
 Fractional Excretion ratios of eight protein biomarkers in SLE patients and controls. Fractional excretion (FE) ratios of all 8 biomarker proteins were calculated by dividing the urine biomarker levels by the corresponding serum biomarker levels, after normalizing both against urine or serum creatinine, respectively. The Y axes show the values of the fractional excretion ratios of studied biomarkers as well as their SE (error bars), while the X axes display the 4 groups interrogated (25 healthy controls; 32 inactive SLE; 31 active non-renal disease; 33 active renal disease). * = P < 0.05, ** = P < 0.01, *** = P < 0.001, **** = P < 0.0001.
Fractional Excretion ratios of eight protein biomarkers in SLE patients and controls. Fractional excretion (FE) ratios of all 8 biomarker proteins were calculated by dividing the urine biomarker levels by the corresponding serum biomarker levels, after normalizing both against urine or serum creatinine, respectively. The Y axes show the values of the fractional excretion ratios of studied biomarkers as well as their SE (error bars), while the X axes display the 4 groups interrogated (25 healthy controls; 32 inactive SLE; 31 active non-renal disease; 33 active renal disease). * = P < 0.05, ** = P < 0.01, *** = P < 0.001, **** = P < 0.0001. Correlation of Fractional Excretion (FE) ratios of eight protein biomarkers with conventional disease activity measures in SLE. The derived FE ratios of the eight interrogated biomarkers were examined for their correlation with SLEDAI, renal-SLEDAI, C3, C4, anti-dsDNA and Physician Global Assessment (PGA) values. Positive and negative correlations are denoted by orange and blue circles respectively, while statistical significance is denoted using grey-scale boxes. Overall, the urine biomarker fractional excretion ratios correlate best with renal-SLEDAI in LN.
Correlation of Fractional Excretion (FE) ratios of eight protein biomarkers with conventional disease activity measures in SLE. The derived FE ratios of the eight interrogated biomarkers were examined for their correlation with SLEDAI, renal-SLEDAI, C3, C4, anti-dsDNA and Physician Global Assessment (PGA) values. Positive and negative correlations are denoted by orange and blue circles respectively, while statistical significance is denoted using grey-scale boxes. Overall, the urine biomarker fractional excretion ratios correlate best with renal-SLEDAI in LN.  Comparing the diagnostic potential of FE ratios and their corresponding urine biomarkers in identifying active LN. Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curves were generated for the 8 urine protein markers (blue line) and their corresponding FE ratios (red line) in differentiating active lupus nephritis from inactive SLE (top) and active lupus nephritis from all other SLE patients (active non-renal and inactive SLE) (bottom)
Comparing the diagnostic potential of FE ratios and their corresponding urine biomarkers in identifying active LN. Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curves were generated for the 8 urine protein markers (blue line) and their corresponding FE ratios (red line) in differentiating active lupus nephritis from inactive SLE (top) and active lupus nephritis from all other SLE patients (active non-renal and inactive SLE) (bottom)Disclosures: S. Soliman, None; S. Stanley, None; K. Vanarsa, None; F. Ismail, None; C. Mok, None; C. mohan, None.

