Back
Poster Session B
Infection-related rheumatic syndromes
Session: (0779–0806) Infection-related Rheumatic Disease Poster
0780: B-cell Reconstitution Is Associated with COVID-19 Booster Vaccine Responsiveness in Previously Seronegative Rituximab Treated Rheumatic Disease Patients
Sunday, November 13, 2022
9:00 AM – 10:30 AM Eastern Time
Location: Virtual Poster Hall
- KS
Kaitlin Schultz, BA
Hospital for Special Surgery
New York, NY, United States
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Kaitlin Schultz, Deanna Jannat-Khah, DrPH, MSPH and Robert Spiera, Hospital for Special Surgery, New York, NY
Background/Purpose: Booster doses of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines continue to serve as an important strategy for containing the pandemic and may be especially important to rituximab treated patients. B-cell depletion has been associated with worse outcomes from COVID-19 infection, and many rituximab treated patients demonstrate an inadequate serologic response to the initial vaccine series. Strategies to optimize serologic response to COVID-19 vaccine boosters in previously serologically unresponsive patients is, therefore, of particular relevance. In this retrospective study, we aimed to assess factors associated with serologic response to COVID-19 booster vaccines in rituximab treated patients previously serologically unresponsive to the initial vaccine series.
Methods: A retrospective chart review of rituximab-treated patients who failed to demonstrate a serologic response to the first SARS-CoV-2 vaccination series and subsequently received an mRNA vaccine booster was performed. Serologic response four weeks or more after the booster was the primary outcome. T-tests, Fisher's exact tests, and Wilcoxon rank sum tests were used for comparisons. Box and whisker plots were constructed to visualize differences between serologic response.
Results: In 31 rituximab treated patients who were seronegative following the initial vaccine series, demographic characteristics, concurrent therapies, rheumatologic diagnosis, and vaccine type were not associated with serologic positivity to the booster vaccine (Table 1). Ten patients (32%) were defined as being hypogammaglobulinemic (Immunoglobulin G < 700 mg/dL) whereas no patients were lymphopenic (Absolute Lymphocyte < 0.9 K/uL) (Table 1). Absolute lymphocyte levels were not statistically different between vaccine responders and non-responders (p=0.21). IgG levels were lower in patients without a serologic response than in those who did seroconvert (689 mg/dL, IQR (651 ,757) vs 928, IQR (735, 1001), p=0.018). B-cell reconstitution was significantly different between those with positive (median, IQR 1.785 (0.65, 3)) and negative (median, IQR 0 (0,0)) serologic responses to the booster (p-value< 0.001) as was time from last rituximab exposure (p-value = 0.030) (Figure 1). Positive predictive value of B-cell presence was 90.9% (95% CI: 70.8%, 98.9%) and negative predictive value was 100% (95% CI: 59%, 100%) for serologic response to the mRNA booster. Positive predictive value of time >6 months from last rituximab to the booster was 78.3% (95% CI 56.3%, 92.5%) and the negative predictive value was 62.5% (95% CI 24.5%, 91.5%).
Conclusion: Presence of detectable B-cells and longer time from last rituximab were associated with the development of SARS-CoV-2 anti-spike protein antibodies following the booster vaccine. These factors should be considered in timing of administration of booster vaccine doses in previously unresponsive rituximab-treated patients.
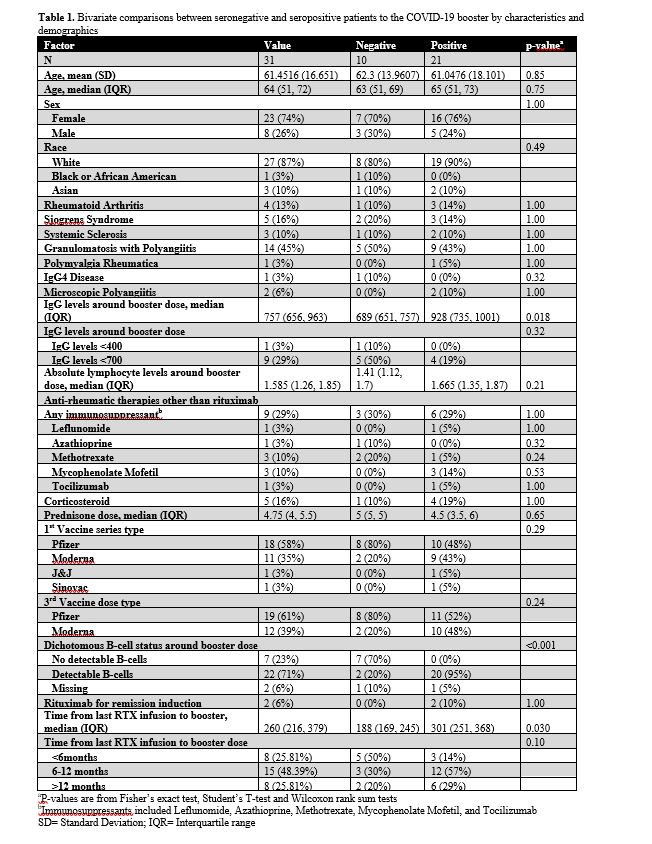 Demographics, concurrent therapies, rheumatologic diagnosis, absolute lymphocyte levels, and vaccine type were not associated with serologic positivity to the booster vaccine. B-cell reconstitution was significantly different between those with positive and negative serologic responses to the booster (p-value < 0.001) as was time from last rituximab exposure (p-value = 0.030). Wilcoxon rank sum test was used to calculate the p-value.
Demographics, concurrent therapies, rheumatologic diagnosis, absolute lymphocyte levels, and vaccine type were not associated with serologic positivity to the booster vaccine. B-cell reconstitution was significantly different between those with positive and negative serologic responses to the booster (p-value < 0.001) as was time from last rituximab exposure (p-value = 0.030). Wilcoxon rank sum test was used to calculate the p-value.
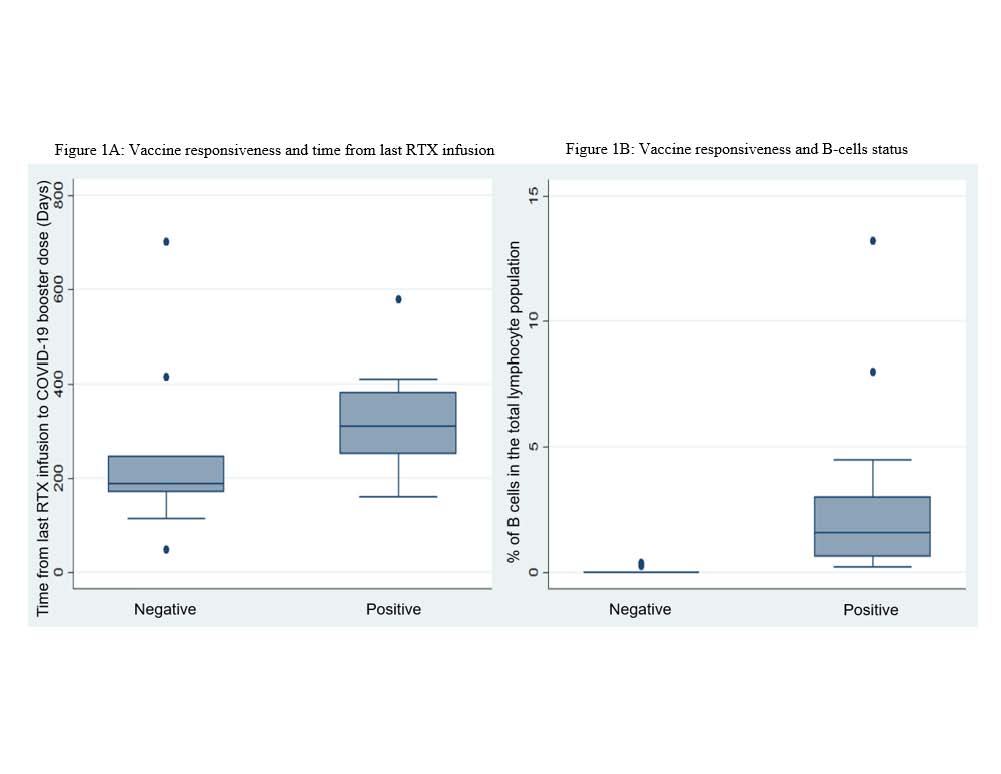 (A) Among patients with a negative serologic response, the median IQR of days from last infusion to COVID-19 booster vaccination was 188 (169, 245) days. Patients with a positive serologic response had a median IQR of 301 (251,368) days. Wilcoxon rank sum test was used to calculate the p-value. (B) The percentage of B-cells among the negative serologic response median IQR was 0 (0,0). Among the positive serologic vaccine response group, the median IQR was 1.785 (0.65, 3). The p-value is from the Wilcoxon rank sum test. The Y-axis is the percentage of B-cells in the total lymphocyte population.
(A) Among patients with a negative serologic response, the median IQR of days from last infusion to COVID-19 booster vaccination was 188 (169, 245) days. Patients with a positive serologic response had a median IQR of 301 (251,368) days. Wilcoxon rank sum test was used to calculate the p-value. (B) The percentage of B-cells among the negative serologic response median IQR was 0 (0,0). Among the positive serologic vaccine response group, the median IQR was 1.785 (0.65, 3). The p-value is from the Wilcoxon rank sum test. The Y-axis is the percentage of B-cells in the total lymphocyte population.
Disclosures: K. Schultz, None; D. Jannat-Khah, DrPH, MSPH, Cytodyn, AstraZeneca, Walgreens; R. Spiera, GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), Boehringer-Ingelheim, Corbus Pharmaceutical, InflaRx, AbbVie/Abbott, Sanofi, Novartis, Chemocentryx, Roche, Vera.
Background/Purpose: Booster doses of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines continue to serve as an important strategy for containing the pandemic and may be especially important to rituximab treated patients. B-cell depletion has been associated with worse outcomes from COVID-19 infection, and many rituximab treated patients demonstrate an inadequate serologic response to the initial vaccine series. Strategies to optimize serologic response to COVID-19 vaccine boosters in previously serologically unresponsive patients is, therefore, of particular relevance. In this retrospective study, we aimed to assess factors associated with serologic response to COVID-19 booster vaccines in rituximab treated patients previously serologically unresponsive to the initial vaccine series.
Methods: A retrospective chart review of rituximab-treated patients who failed to demonstrate a serologic response to the first SARS-CoV-2 vaccination series and subsequently received an mRNA vaccine booster was performed. Serologic response four weeks or more after the booster was the primary outcome. T-tests, Fisher's exact tests, and Wilcoxon rank sum tests were used for comparisons. Box and whisker plots were constructed to visualize differences between serologic response.
Results: In 31 rituximab treated patients who were seronegative following the initial vaccine series, demographic characteristics, concurrent therapies, rheumatologic diagnosis, and vaccine type were not associated with serologic positivity to the booster vaccine (Table 1). Ten patients (32%) were defined as being hypogammaglobulinemic (Immunoglobulin G < 700 mg/dL) whereas no patients were lymphopenic (Absolute Lymphocyte < 0.9 K/uL) (Table 1). Absolute lymphocyte levels were not statistically different between vaccine responders and non-responders (p=0.21). IgG levels were lower in patients without a serologic response than in those who did seroconvert (689 mg/dL, IQR (651 ,757) vs 928, IQR (735, 1001), p=0.018). B-cell reconstitution was significantly different between those with positive (median, IQR 1.785 (0.65, 3)) and negative (median, IQR 0 (0,0)) serologic responses to the booster (p-value< 0.001) as was time from last rituximab exposure (p-value = 0.030) (Figure 1). Positive predictive value of B-cell presence was 90.9% (95% CI: 70.8%, 98.9%) and negative predictive value was 100% (95% CI: 59%, 100%) for serologic response to the mRNA booster. Positive predictive value of time >6 months from last rituximab to the booster was 78.3% (95% CI 56.3%, 92.5%) and the negative predictive value was 62.5% (95% CI 24.5%, 91.5%).
Conclusion: Presence of detectable B-cells and longer time from last rituximab were associated with the development of SARS-CoV-2 anti-spike protein antibodies following the booster vaccine. These factors should be considered in timing of administration of booster vaccine doses in previously unresponsive rituximab-treated patients.
 Demographics, concurrent therapies, rheumatologic diagnosis, absolute lymphocyte levels, and vaccine type were not associated with serologic positivity to the booster vaccine. B-cell reconstitution was significantly different between those with positive and negative serologic responses to the booster (p-value < 0.001) as was time from last rituximab exposure (p-value = 0.030). Wilcoxon rank sum test was used to calculate the p-value.
Demographics, concurrent therapies, rheumatologic diagnosis, absolute lymphocyte levels, and vaccine type were not associated with serologic positivity to the booster vaccine. B-cell reconstitution was significantly different between those with positive and negative serologic responses to the booster (p-value < 0.001) as was time from last rituximab exposure (p-value = 0.030). Wilcoxon rank sum test was used to calculate the p-value. (A) Among patients with a negative serologic response, the median IQR of days from last infusion to COVID-19 booster vaccination was 188 (169, 245) days. Patients with a positive serologic response had a median IQR of 301 (251,368) days. Wilcoxon rank sum test was used to calculate the p-value. (B) The percentage of B-cells among the negative serologic response median IQR was 0 (0,0). Among the positive serologic vaccine response group, the median IQR was 1.785 (0.65, 3). The p-value is from the Wilcoxon rank sum test. The Y-axis is the percentage of B-cells in the total lymphocyte population.
(A) Among patients with a negative serologic response, the median IQR of days from last infusion to COVID-19 booster vaccination was 188 (169, 245) days. Patients with a positive serologic response had a median IQR of 301 (251,368) days. Wilcoxon rank sum test was used to calculate the p-value. (B) The percentage of B-cells among the negative serologic response median IQR was 0 (0,0). Among the positive serologic vaccine response group, the median IQR was 1.785 (0.65, 3). The p-value is from the Wilcoxon rank sum test. The Y-axis is the percentage of B-cells in the total lymphocyte population.Disclosures: K. Schultz, None; D. Jannat-Khah, DrPH, MSPH, Cytodyn, AstraZeneca, Walgreens; R. Spiera, GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), Boehringer-Ingelheim, Corbus Pharmaceutical, InflaRx, AbbVie/Abbott, Sanofi, Novartis, Chemocentryx, Roche, Vera.

