Back
Abstract Session
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
Session: Abstracts: SLE – Animal Models (1663–1666)
1664: TRIM21 as a Regulator of UVB-Driven IFN Responses in Lupus
Monday, November 14, 2022
10:45 AM – 10:55 AM Eastern Time
Location: Room 114 Nutter Theatre
- RM
Richard Moore, BSc
Cedars-Sinai
Los Angeles, CA, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Richard Moore, Gantsetseg Tumurkhuu, Daniel Wallace and Caroline Jefferies, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA
Background/Purpose: Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) experience photosensitivity where exposure to ultraviolet light B (UVB) drives lupus flares and systemic symptoms. Although the mechanisms linking UVB exposure to these effects are unclear, type I IFNs are known to play a role. TRIM21, an autoantigen in SLE, functions as a negative regulator on the pathways driving IFN expression. Here we explore that the E3 ligase TRIM21 functions to regulate both local and systemic inflammation following UVB exposure in mice and altered expression may explain photosensitivity in SLE.
Methods: C57BL/6 Trim21+/+ (WT) and Trim21-/- (KO) mice were irradiated with UVB (100 mJ/cm2) on shaved dorsal skin with inflammatory responses measured by mRNA transcript levels, histology, and flow cytometry. To determine molecular targets of TRIM21 after UVB exposure, bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) and murine dermal fibroblasts (MDFs) were isolated from WT and KO mice and treated with the stimulator of IFN genes (STING)-agonist cyclic GMP-AMP (cGAMP) or 100 mJ/cm2 UVB, respectively. Lysates of these cells were used to determine direct effects of intracellular signaling pathways via immunoblotting and immunoprecipitation.
Results: Erythema and edema developed in UVB-exposed skin of both WT and KO mice and associated with increased immune infiltrate within the skin (Fig 1A). However, UVB-exposed skin of KO mice showed increased local levels of conventional dendritic cells, myeloid activation, IFN-stimulated genes (ISGs), and IgG deposition (Fig 1B-D). This response led us to investigate the systemic effects of UVB exposure and indeed, circulating cytokines and activation markers on both circulating monocytes and neutrophils within the spleen were significantly increased (Fig 2A-C). Further, increased levels of both neutrophils and CD4+ T cells were detected in the KO spleen (Fig 2C).
Because we observed local and systemic inflammation, we sought the role TRIM21 has during these processes. To do this, we stimulated MDFs and BMDMs with UVB or cGAS, respectively, and measured protein levels of a known target of TRIM21 E3 ligase activity (DDX41) and phosphorylation of a downstream effector of the STING pathway (TBK1) as well as Ifnb transcript levels. While KO MDFs and BMDMs exhibited increased responses to stimulation, specific inhibition of STING with H151 ameliorated these effects (Fig 3).
Conclusion: In this work, we investigated the effect of Trim21 deficiency in the pathogenesis of the lupus UVB mouse model. Trim21-deficient mice developed heightened local and systemic response to chronic UVB exposure compared to WT mice. Our preliminary analyses confirmed this phenotype is rescued by STING inhibition, keeping with the importance of STING in UVB-driven IFN responses. Taken together, loss of TRIM21 exacerbates UVB-induced skin and systemic inflammation as a result of dysregulated IFN responses in innate immune signaling.
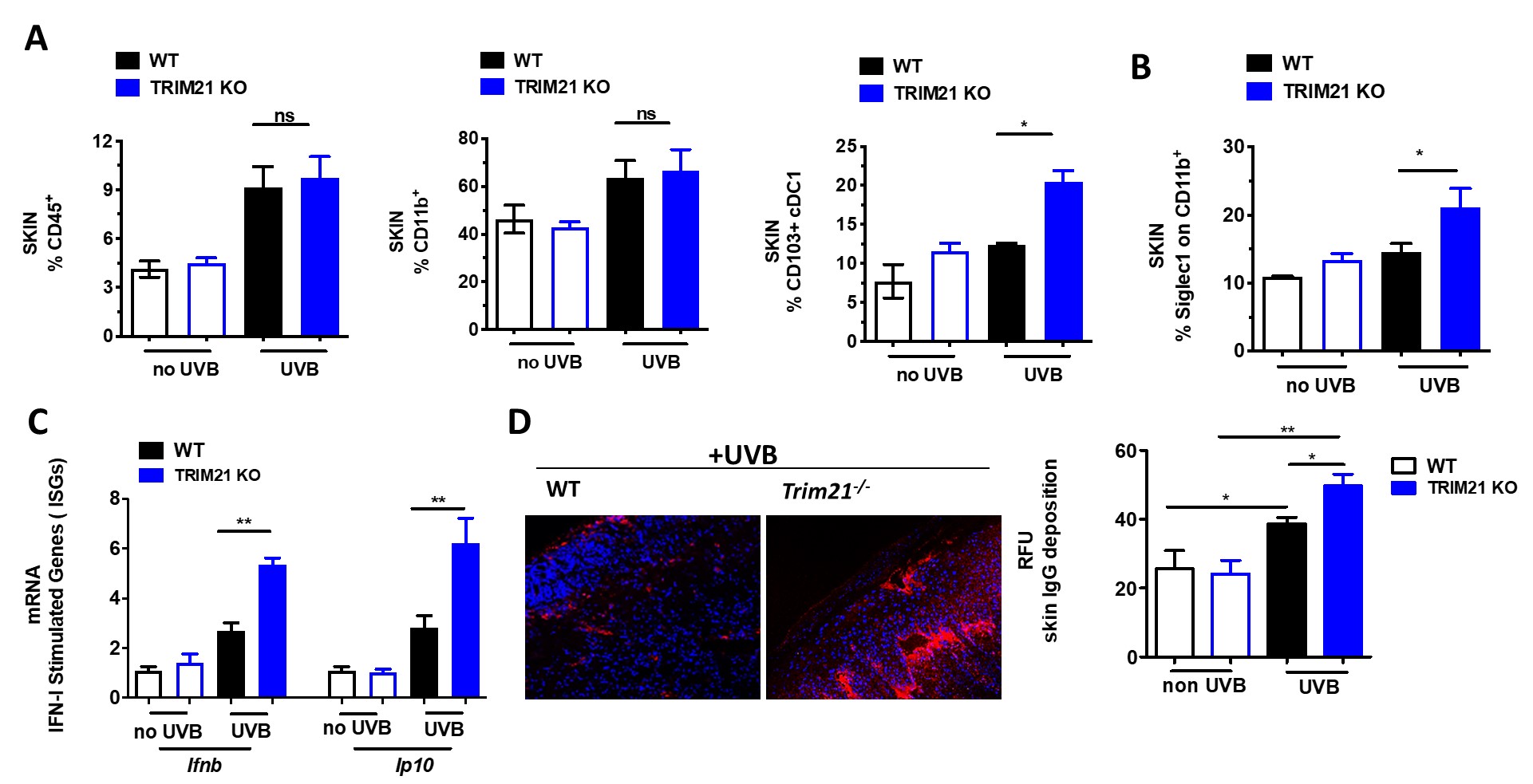 Figure 1. C57BL/6 Trim21+/+ (WT) and Trim21-/- (TRIM21 KO) mice were exposed to UVB irradiation. (A) Flow cytometry analysis following the final UVB dose showing the percentage of infiltrating immune cells (CD45+) , myeloid cells (CD11b+), dendritic cells (CD45+CD11C+MHCII+CD103+). (B) The percentage of Siglec1, an IFN-inducible protein, on CD11b+ skin infiltrating cells. (C) Cutaneous expression of mRNA for IFN inducible genes (ISGs) genes following UVB injury, as determined by qPCR. Fold change was calculated against nonirradiated mice, using the 2−ΔΔCt method. Data are compiled from at least 3 independent experiments. (D) IgG deposition in UVB induced skin lesion. A representative pictures and quantification analysis. Values are the mean ± SD. *p < 0.05; versus no UV irradiation, One-Way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
Figure 1. C57BL/6 Trim21+/+ (WT) and Trim21-/- (TRIM21 KO) mice were exposed to UVB irradiation. (A) Flow cytometry analysis following the final UVB dose showing the percentage of infiltrating immune cells (CD45+) , myeloid cells (CD11b+), dendritic cells (CD45+CD11C+MHCII+CD103+). (B) The percentage of Siglec1, an IFN-inducible protein, on CD11b+ skin infiltrating cells. (C) Cutaneous expression of mRNA for IFN inducible genes (ISGs) genes following UVB injury, as determined by qPCR. Fold change was calculated against nonirradiated mice, using the 2−ΔΔCt method. Data are compiled from at least 3 independent experiments. (D) IgG deposition in UVB induced skin lesion. A representative pictures and quantification analysis. Values are the mean ± SD. *p < 0.05; versus no UV irradiation, One-Way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
.jpg) Figure 2. C57BL/6 Trim21+/+ (WT) and Trim21-/- (TRIM21 KO) mice were exposed to UVB irradiation. (A) Compared to WT mice, Trim21-/- mice post-UVB exposure had higher circulating monocytes and increased inflammatory markers CCR2 and Siglec1 in Ly6Chi and CD11b+ cells, respectively. (B) Inflammatory cytokines post-UVB determined by Legendflex assay. (C) FACS analysis of spleens following UVB exposure. n = 5-6 per group. All data represent mean ± SD. Statistical significance was determined using One-Way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test . *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
Figure 2. C57BL/6 Trim21+/+ (WT) and Trim21-/- (TRIM21 KO) mice were exposed to UVB irradiation. (A) Compared to WT mice, Trim21-/- mice post-UVB exposure had higher circulating monocytes and increased inflammatory markers CCR2 and Siglec1 in Ly6Chi and CD11b+ cells, respectively. (B) Inflammatory cytokines post-UVB determined by Legendflex assay. (C) FACS analysis of spleens following UVB exposure. n = 5-6 per group. All data represent mean ± SD. Statistical significance was determined using One-Way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test . *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
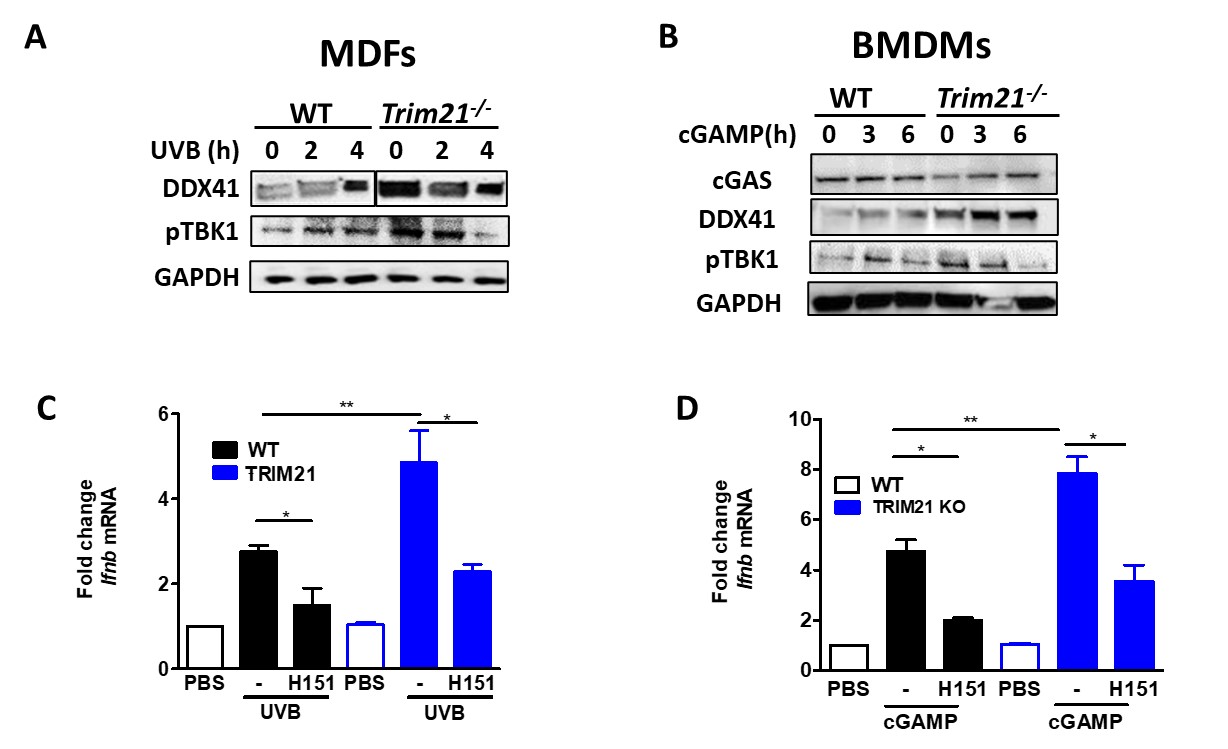 Figure 3. Mouse Dermal Fibroblasts (MDFs) and bone marrow derived macrophages (BMDM) derived from WT and Trim21-/- mice were stimulated with UVB or cGAMP for indicated hours. (A-B) The levels of DDX41, cGAS and pTBK1 were determined by immunoblotting. (C-D) The expression of Ifnb mRNA was determined by qPCR. All data represent mean ± SD. Statistical significance was determined using t-test in A; One-Way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test in B . *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
Figure 3. Mouse Dermal Fibroblasts (MDFs) and bone marrow derived macrophages (BMDM) derived from WT and Trim21-/- mice were stimulated with UVB or cGAMP for indicated hours. (A-B) The levels of DDX41, cGAS and pTBK1 were determined by immunoblotting. (C-D) The expression of Ifnb mRNA was determined by qPCR. All data represent mean ± SD. Statistical significance was determined using t-test in A; One-Way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test in B . *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
Disclosures: R. Moore, None; G. Tumurkhuu, None; D. Wallace, None; C. Jefferies, None.
Background/Purpose: Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) experience photosensitivity where exposure to ultraviolet light B (UVB) drives lupus flares and systemic symptoms. Although the mechanisms linking UVB exposure to these effects are unclear, type I IFNs are known to play a role. TRIM21, an autoantigen in SLE, functions as a negative regulator on the pathways driving IFN expression. Here we explore that the E3 ligase TRIM21 functions to regulate both local and systemic inflammation following UVB exposure in mice and altered expression may explain photosensitivity in SLE.
Methods: C57BL/6 Trim21+/+ (WT) and Trim21-/- (KO) mice were irradiated with UVB (100 mJ/cm2) on shaved dorsal skin with inflammatory responses measured by mRNA transcript levels, histology, and flow cytometry. To determine molecular targets of TRIM21 after UVB exposure, bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) and murine dermal fibroblasts (MDFs) were isolated from WT and KO mice and treated with the stimulator of IFN genes (STING)-agonist cyclic GMP-AMP (cGAMP) or 100 mJ/cm2 UVB, respectively. Lysates of these cells were used to determine direct effects of intracellular signaling pathways via immunoblotting and immunoprecipitation.
Results: Erythema and edema developed in UVB-exposed skin of both WT and KO mice and associated with increased immune infiltrate within the skin (Fig 1A). However, UVB-exposed skin of KO mice showed increased local levels of conventional dendritic cells, myeloid activation, IFN-stimulated genes (ISGs), and IgG deposition (Fig 1B-D). This response led us to investigate the systemic effects of UVB exposure and indeed, circulating cytokines and activation markers on both circulating monocytes and neutrophils within the spleen were significantly increased (Fig 2A-C). Further, increased levels of both neutrophils and CD4+ T cells were detected in the KO spleen (Fig 2C).
Because we observed local and systemic inflammation, we sought the role TRIM21 has during these processes. To do this, we stimulated MDFs and BMDMs with UVB or cGAS, respectively, and measured protein levels of a known target of TRIM21 E3 ligase activity (DDX41) and phosphorylation of a downstream effector of the STING pathway (TBK1) as well as Ifnb transcript levels. While KO MDFs and BMDMs exhibited increased responses to stimulation, specific inhibition of STING with H151 ameliorated these effects (Fig 3).
Conclusion: In this work, we investigated the effect of Trim21 deficiency in the pathogenesis of the lupus UVB mouse model. Trim21-deficient mice developed heightened local and systemic response to chronic UVB exposure compared to WT mice. Our preliminary analyses confirmed this phenotype is rescued by STING inhibition, keeping with the importance of STING in UVB-driven IFN responses. Taken together, loss of TRIM21 exacerbates UVB-induced skin and systemic inflammation as a result of dysregulated IFN responses in innate immune signaling.
 Figure 1. C57BL/6 Trim21+/+ (WT) and Trim21-/- (TRIM21 KO) mice were exposed to UVB irradiation. (A) Flow cytometry analysis following the final UVB dose showing the percentage of infiltrating immune cells (CD45+) , myeloid cells (CD11b+), dendritic cells (CD45+CD11C+MHCII+CD103+). (B) The percentage of Siglec1, an IFN-inducible protein, on CD11b+ skin infiltrating cells. (C) Cutaneous expression of mRNA for IFN inducible genes (ISGs) genes following UVB injury, as determined by qPCR. Fold change was calculated against nonirradiated mice, using the 2−ΔΔCt method. Data are compiled from at least 3 independent experiments. (D) IgG deposition in UVB induced skin lesion. A representative pictures and quantification analysis. Values are the mean ± SD. *p < 0.05; versus no UV irradiation, One-Way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
Figure 1. C57BL/6 Trim21+/+ (WT) and Trim21-/- (TRIM21 KO) mice were exposed to UVB irradiation. (A) Flow cytometry analysis following the final UVB dose showing the percentage of infiltrating immune cells (CD45+) , myeloid cells (CD11b+), dendritic cells (CD45+CD11C+MHCII+CD103+). (B) The percentage of Siglec1, an IFN-inducible protein, on CD11b+ skin infiltrating cells. (C) Cutaneous expression of mRNA for IFN inducible genes (ISGs) genes following UVB injury, as determined by qPCR. Fold change was calculated against nonirradiated mice, using the 2−ΔΔCt method. Data are compiled from at least 3 independent experiments. (D) IgG deposition in UVB induced skin lesion. A representative pictures and quantification analysis. Values are the mean ± SD. *p < 0.05; versus no UV irradiation, One-Way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. .jpg) Figure 2. C57BL/6 Trim21+/+ (WT) and Trim21-/- (TRIM21 KO) mice were exposed to UVB irradiation. (A) Compared to WT mice, Trim21-/- mice post-UVB exposure had higher circulating monocytes and increased inflammatory markers CCR2 and Siglec1 in Ly6Chi and CD11b+ cells, respectively. (B) Inflammatory cytokines post-UVB determined by Legendflex assay. (C) FACS analysis of spleens following UVB exposure. n = 5-6 per group. All data represent mean ± SD. Statistical significance was determined using One-Way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test . *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
Figure 2. C57BL/6 Trim21+/+ (WT) and Trim21-/- (TRIM21 KO) mice were exposed to UVB irradiation. (A) Compared to WT mice, Trim21-/- mice post-UVB exposure had higher circulating monocytes and increased inflammatory markers CCR2 and Siglec1 in Ly6Chi and CD11b+ cells, respectively. (B) Inflammatory cytokines post-UVB determined by Legendflex assay. (C) FACS analysis of spleens following UVB exposure. n = 5-6 per group. All data represent mean ± SD. Statistical significance was determined using One-Way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test . *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Figure 3. Mouse Dermal Fibroblasts (MDFs) and bone marrow derived macrophages (BMDM) derived from WT and Trim21-/- mice were stimulated with UVB or cGAMP for indicated hours. (A-B) The levels of DDX41, cGAS and pTBK1 were determined by immunoblotting. (C-D) The expression of Ifnb mRNA was determined by qPCR. All data represent mean ± SD. Statistical significance was determined using t-test in A; One-Way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test in B . *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
Figure 3. Mouse Dermal Fibroblasts (MDFs) and bone marrow derived macrophages (BMDM) derived from WT and Trim21-/- mice were stimulated with UVB or cGAMP for indicated hours. (A-B) The levels of DDX41, cGAS and pTBK1 were determined by immunoblotting. (C-D) The expression of Ifnb mRNA was determined by qPCR. All data represent mean ± SD. Statistical significance was determined using t-test in A; One-Way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test in B . *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.Disclosures: R. Moore, None; G. Tumurkhuu, None; D. Wallace, None; C. Jefferies, None.

