Back
Poster Session D
Immunobiology
Session: (1681–1706) Innate Immunity Poster: Basic and Translational Science
1685: The Presence of Anti-MAA Antibodies to Extracellular Matrix Proteins in Synovial Fluid and Sera of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
Monday, November 14, 2022
1:00 PM – 3:00 PM Eastern Time
Location: Virtual Poster Hall
- AT
Alexandra Taylor, BS
Creighton University School of Medicine
Omaha, NE, United States
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Alexandra Taylor1, Michael Duryee2, Carlos Hunter2, nozima Aripova2, Ted Mikuls3 and Geoffrey Thiele2, 1Creighton University School of Medicine, Omaha, NE, 2University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha, NE, 3Division of Rheumatology, University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha, NE
Background/Purpose: Antibodies to malondialdehyde-acetaldehyde protein adducts (MAA) are increased in both the serum and synovial joint fluid from patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA). These antibodies strongly associate with disease activity and have been demonstrated to predict disease onset. Immunohistochemical (IHC) staining of RA joint tissues for MAA have suggested that extracellular matrix proteins (ECM) are involved in the disease pathogenesis. However, these studies only examined the associations of MAA and ECM proteins to co-localize together in the same area of the joint. Therefore, it was the purpose of this study to determine whether RA patients develop antibodies to MAA modified ECM proteins in the serum and synovial fluid.
Methods: ELISA plates were coated with MAA modified collagen II, vimentin, fibrinogen and incubated overnight at 4oC degrees. Matched serum and synovial fluid from RA patients and OA controls were incubated with the antigen coated plates. Secondary antibodies specific to human IgG, IgM and IgA were added to determine isotype involvement. Detection was accomplished using horseradish peroxidase (HRP) labeled goat anti-human IgG, IgM, or IgA antibodies. Absorbance was determined at 450 nm using an Epoch Plate reader (BioTek) and analyzed using Gene 5 Software (BioTek). Data are expressed in arbitrary units (AU) of MAA antibody relative to the standard curve.
Results: Circulating serum IgG antibodies to MAA adducted ECM proteins were significantly increased in the RA patients compared to OA, CII p< 0.05, VIM p< 0.0001, FIB p< 0.0001. Similar results were observed in the RA synovial fluid compared to the OA, CII p< 0.05, VIM p< 0.0001, FIB p< 0.05. IgM antibodies to ECM proteins in the RA patients demonstrated a significant increase in CII p=NS, VIM p< 0.001, FIB p< 0.01 for both serum and synovial fluid compared to the OA. However, IgA antibodies to ECM proteins showed a unique profile. RA synovial fluid had higher antibodies in CII p< 0.01 compared to serum for both RA and OA patients. Antibodies to FIB were significantly p< 0.01 decreased in the RA synovial fluid compared to OA. Yet, antibodies to VIM were both increased in the serum (p< 0.05) and synovial fluid (P< 0.01) in the RA samples compared to OA. Importantly, vimentin MAA demonstrated the highest antibody concentration for all of the ECM proteins evaluated.
Conclusion: Identification of serum antibodies to MAA modified ECM proteins in the synovial fluid and serum of RA patients provides new insight into the onset or progression of RA. These modified proteins and antibodies to them may be potential biomarkers for the diagnosis/treatment of patients with RA. Further work is needed to elucidate the role these modified proteins are playing in the manifestation of this disease.
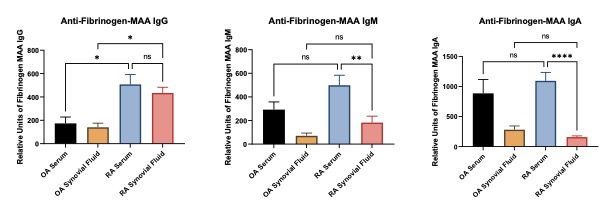 Figure 1. ELISA to determine the reactivity to the anti-Fibrinogen MAA antibodies in Serum and Synovial Fluid from OA and RA Patients. Plates were coated with MAA modified fibrinogen and allowed to react with synovial fluid or serum taken from OA or RA patients to determine binding of circulating antibodies. (A) Anti-fibrinogen IgG was significantly *p < 0.05 increase in the RA serum compared to OA serum and synovial fluid and RA synovial fluid. RA synovial fluid was significantly increased ****p < 0.0001 compare to OA fluid. (B) Anti-fibrinogen IgM was significantly **p < 0.01 increase in the RA serum compared to OA serum and synovial fluid and RA synovial fluid. RA synovial fluid was significantly increased **p < 0.01 compare to OA fluid. (C) Anti-fibrinogen was significantly **p < 0.01 increase in the and synovial fluid and RA synovial fluid. RA synovial fluid was not increased compare to OA fluid.
Figure 1. ELISA to determine the reactivity to the anti-Fibrinogen MAA antibodies in Serum and Synovial Fluid from OA and RA Patients. Plates were coated with MAA modified fibrinogen and allowed to react with synovial fluid or serum taken from OA or RA patients to determine binding of circulating antibodies. (A) Anti-fibrinogen IgG was significantly *p < 0.05 increase in the RA serum compared to OA serum and synovial fluid and RA synovial fluid. RA synovial fluid was significantly increased ****p < 0.0001 compare to OA fluid. (B) Anti-fibrinogen IgM was significantly **p < 0.01 increase in the RA serum compared to OA serum and synovial fluid and RA synovial fluid. RA synovial fluid was significantly increased **p < 0.01 compare to OA fluid. (C) Anti-fibrinogen was significantly **p < 0.01 increase in the and synovial fluid and RA synovial fluid. RA synovial fluid was not increased compare to OA fluid.
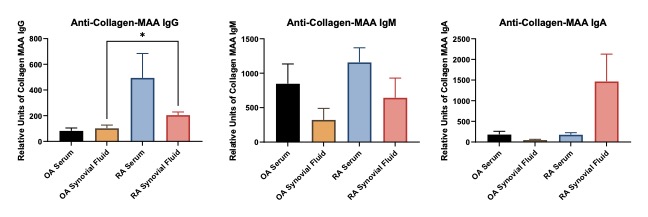 Figure 2. ELISA to determine the reactivity to the anti-Collagen II MAA antibodies in Serum and Synovial Fluid from OA and RA Patients. Plates were coated with MAA modified collagen II and allowed to react with synovial fluid or serum taken from OA or RA patients to determine binding of circulating antibodies. (A) Anti-collagen IgG was significantly *p < 0.05 increase in the RA serum compared to OA serum and synovial fluid and RA synovial fluid. (B) Anti-collagen IgM was increased in the RA serum compared to all other groups, yet significance was not reached. (C) Anti-collagen IgA was increased in the RA synovial fluid compared to all other groups, yet there was a lot variability in the data making it not significant.
Figure 2. ELISA to determine the reactivity to the anti-Collagen II MAA antibodies in Serum and Synovial Fluid from OA and RA Patients. Plates were coated with MAA modified collagen II and allowed to react with synovial fluid or serum taken from OA or RA patients to determine binding of circulating antibodies. (A) Anti-collagen IgG was significantly *p < 0.05 increase in the RA serum compared to OA serum and synovial fluid and RA synovial fluid. (B) Anti-collagen IgM was increased in the RA serum compared to all other groups, yet significance was not reached. (C) Anti-collagen IgA was increased in the RA synovial fluid compared to all other groups, yet there was a lot variability in the data making it not significant.
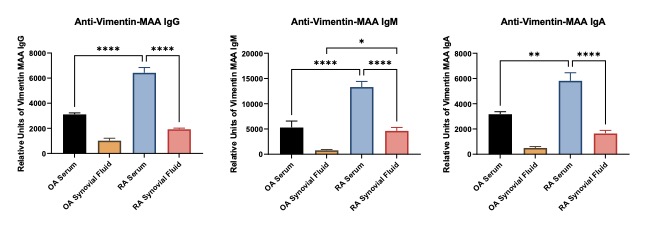 Figure 3. ELISA to determine the reactivity to the anti-Vimentin MAA antibodies in Serum and Synovial Fluid from OA and RA Patients. Plates were coated with MAA modified vimentin and allowed to react with synovial fluid or serum taken from OA or RA patients to determine binding of circulating antibodies. (A) Anti-vimentin IgG was significantly ****p < 0.0001 increase in the RA serum compared to OA serum and synovial fluid and RA synovial fluid. RA synovial fluid was significantly increased ****p < 0.0001 compare to OA fluid. (B) Anti-vimentin IgM was significantly ***p < 0.001 increase in the RA serum compared to OA serum and synovial fluid and RA synovial fluid. RA synovial fluid was significantly increased ***p < 0.001 compare to OA fluid. (C) Anti-vimentin was significantly *p < 0.05 increase in the RA serum compared to OA serum and synovial fluid and RA synovial fluid. RA synovial fluid was significantly increased **p < 0.01 compare to OA fluid.
Figure 3. ELISA to determine the reactivity to the anti-Vimentin MAA antibodies in Serum and Synovial Fluid from OA and RA Patients. Plates were coated with MAA modified vimentin and allowed to react with synovial fluid or serum taken from OA or RA patients to determine binding of circulating antibodies. (A) Anti-vimentin IgG was significantly ****p < 0.0001 increase in the RA serum compared to OA serum and synovial fluid and RA synovial fluid. RA synovial fluid was significantly increased ****p < 0.0001 compare to OA fluid. (B) Anti-vimentin IgM was significantly ***p < 0.001 increase in the RA serum compared to OA serum and synovial fluid and RA synovial fluid. RA synovial fluid was significantly increased ***p < 0.001 compare to OA fluid. (C) Anti-vimentin was significantly *p < 0.05 increase in the RA serum compared to OA serum and synovial fluid and RA synovial fluid. RA synovial fluid was significantly increased **p < 0.01 compare to OA fluid.
Disclosures: A. Taylor, None; M. Duryee, None; C. Hunter, None; n. Aripova, None; T. Mikuls, Gilead Sciences, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Horizon, Sanofi, Pfizer Inc; G. Thiele, None.
Background/Purpose: Antibodies to malondialdehyde-acetaldehyde protein adducts (MAA) are increased in both the serum and synovial joint fluid from patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA). These antibodies strongly associate with disease activity and have been demonstrated to predict disease onset. Immunohistochemical (IHC) staining of RA joint tissues for MAA have suggested that extracellular matrix proteins (ECM) are involved in the disease pathogenesis. However, these studies only examined the associations of MAA and ECM proteins to co-localize together in the same area of the joint. Therefore, it was the purpose of this study to determine whether RA patients develop antibodies to MAA modified ECM proteins in the serum and synovial fluid.
Methods: ELISA plates were coated with MAA modified collagen II, vimentin, fibrinogen and incubated overnight at 4oC degrees. Matched serum and synovial fluid from RA patients and OA controls were incubated with the antigen coated plates. Secondary antibodies specific to human IgG, IgM and IgA were added to determine isotype involvement. Detection was accomplished using horseradish peroxidase (HRP) labeled goat anti-human IgG, IgM, or IgA antibodies. Absorbance was determined at 450 nm using an Epoch Plate reader (BioTek) and analyzed using Gene 5 Software (BioTek). Data are expressed in arbitrary units (AU) of MAA antibody relative to the standard curve.
Results: Circulating serum IgG antibodies to MAA adducted ECM proteins were significantly increased in the RA patients compared to OA, CII p< 0.05, VIM p< 0.0001, FIB p< 0.0001. Similar results were observed in the RA synovial fluid compared to the OA, CII p< 0.05, VIM p< 0.0001, FIB p< 0.05. IgM antibodies to ECM proteins in the RA patients demonstrated a significant increase in CII p=NS, VIM p< 0.001, FIB p< 0.01 for both serum and synovial fluid compared to the OA. However, IgA antibodies to ECM proteins showed a unique profile. RA synovial fluid had higher antibodies in CII p< 0.01 compared to serum for both RA and OA patients. Antibodies to FIB were significantly p< 0.01 decreased in the RA synovial fluid compared to OA. Yet, antibodies to VIM were both increased in the serum (p< 0.05) and synovial fluid (P< 0.01) in the RA samples compared to OA. Importantly, vimentin MAA demonstrated the highest antibody concentration for all of the ECM proteins evaluated.
Conclusion: Identification of serum antibodies to MAA modified ECM proteins in the synovial fluid and serum of RA patients provides new insight into the onset or progression of RA. These modified proteins and antibodies to them may be potential biomarkers for the diagnosis/treatment of patients with RA. Further work is needed to elucidate the role these modified proteins are playing in the manifestation of this disease.
 Figure 1. ELISA to determine the reactivity to the anti-Fibrinogen MAA antibodies in Serum and Synovial Fluid from OA and RA Patients. Plates were coated with MAA modified fibrinogen and allowed to react with synovial fluid or serum taken from OA or RA patients to determine binding of circulating antibodies. (A) Anti-fibrinogen IgG was significantly *p < 0.05 increase in the RA serum compared to OA serum and synovial fluid and RA synovial fluid. RA synovial fluid was significantly increased ****p < 0.0001 compare to OA fluid. (B) Anti-fibrinogen IgM was significantly **p < 0.01 increase in the RA serum compared to OA serum and synovial fluid and RA synovial fluid. RA synovial fluid was significantly increased **p < 0.01 compare to OA fluid. (C) Anti-fibrinogen was significantly **p < 0.01 increase in the and synovial fluid and RA synovial fluid. RA synovial fluid was not increased compare to OA fluid.
Figure 1. ELISA to determine the reactivity to the anti-Fibrinogen MAA antibodies in Serum and Synovial Fluid from OA and RA Patients. Plates were coated with MAA modified fibrinogen and allowed to react with synovial fluid or serum taken from OA or RA patients to determine binding of circulating antibodies. (A) Anti-fibrinogen IgG was significantly *p < 0.05 increase in the RA serum compared to OA serum and synovial fluid and RA synovial fluid. RA synovial fluid was significantly increased ****p < 0.0001 compare to OA fluid. (B) Anti-fibrinogen IgM was significantly **p < 0.01 increase in the RA serum compared to OA serum and synovial fluid and RA synovial fluid. RA synovial fluid was significantly increased **p < 0.01 compare to OA fluid. (C) Anti-fibrinogen was significantly **p < 0.01 increase in the and synovial fluid and RA synovial fluid. RA synovial fluid was not increased compare to OA fluid. Figure 2. ELISA to determine the reactivity to the anti-Collagen II MAA antibodies in Serum and Synovial Fluid from OA and RA Patients. Plates were coated with MAA modified collagen II and allowed to react with synovial fluid or serum taken from OA or RA patients to determine binding of circulating antibodies. (A) Anti-collagen IgG was significantly *p < 0.05 increase in the RA serum compared to OA serum and synovial fluid and RA synovial fluid. (B) Anti-collagen IgM was increased in the RA serum compared to all other groups, yet significance was not reached. (C) Anti-collagen IgA was increased in the RA synovial fluid compared to all other groups, yet there was a lot variability in the data making it not significant.
Figure 2. ELISA to determine the reactivity to the anti-Collagen II MAA antibodies in Serum and Synovial Fluid from OA and RA Patients. Plates were coated with MAA modified collagen II and allowed to react with synovial fluid or serum taken from OA or RA patients to determine binding of circulating antibodies. (A) Anti-collagen IgG was significantly *p < 0.05 increase in the RA serum compared to OA serum and synovial fluid and RA synovial fluid. (B) Anti-collagen IgM was increased in the RA serum compared to all other groups, yet significance was not reached. (C) Anti-collagen IgA was increased in the RA synovial fluid compared to all other groups, yet there was a lot variability in the data making it not significant. Figure 3. ELISA to determine the reactivity to the anti-Vimentin MAA antibodies in Serum and Synovial Fluid from OA and RA Patients. Plates were coated with MAA modified vimentin and allowed to react with synovial fluid or serum taken from OA or RA patients to determine binding of circulating antibodies. (A) Anti-vimentin IgG was significantly ****p < 0.0001 increase in the RA serum compared to OA serum and synovial fluid and RA synovial fluid. RA synovial fluid was significantly increased ****p < 0.0001 compare to OA fluid. (B) Anti-vimentin IgM was significantly ***p < 0.001 increase in the RA serum compared to OA serum and synovial fluid and RA synovial fluid. RA synovial fluid was significantly increased ***p < 0.001 compare to OA fluid. (C) Anti-vimentin was significantly *p < 0.05 increase in the RA serum compared to OA serum and synovial fluid and RA synovial fluid. RA synovial fluid was significantly increased **p < 0.01 compare to OA fluid.
Figure 3. ELISA to determine the reactivity to the anti-Vimentin MAA antibodies in Serum and Synovial Fluid from OA and RA Patients. Plates were coated with MAA modified vimentin and allowed to react with synovial fluid or serum taken from OA or RA patients to determine binding of circulating antibodies. (A) Anti-vimentin IgG was significantly ****p < 0.0001 increase in the RA serum compared to OA serum and synovial fluid and RA synovial fluid. RA synovial fluid was significantly increased ****p < 0.0001 compare to OA fluid. (B) Anti-vimentin IgM was significantly ***p < 0.001 increase in the RA serum compared to OA serum and synovial fluid and RA synovial fluid. RA synovial fluid was significantly increased ***p < 0.001 compare to OA fluid. (C) Anti-vimentin was significantly *p < 0.05 increase in the RA serum compared to OA serum and synovial fluid and RA synovial fluid. RA synovial fluid was significantly increased **p < 0.01 compare to OA fluid.Disclosures: A. Taylor, None; M. Duryee, None; C. Hunter, None; n. Aripova, None; T. Mikuls, Gilead Sciences, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Horizon, Sanofi, Pfizer Inc; G. Thiele, None.

