Back
Ignite Talk
Session: Ignite Session 3A
1571: Coronary Arteritis and Periarteritis Secondary to IgG4-related Disease in a Large, Single-center Cohort
Sunday, November 13, 2022
9:40 AM – 9:45 AM Eastern Time
Location: Northern Liberties Stage
- GK
Guy Katz, MD
Massachusetts General Hospital
Boston, MA, United StatesDisclosure: Disclosure(s): No financial relationships with ineligible companies to disclose
Ignite Speaker(s)
Guy Katz1, sandeep hedgire1, James Stone2, Sebastian Perez-Espina1, Ana Fernandes1, Cory Perugino1, Zachary Wallace1 and John Stone3, 1Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA, 2Massachusetts General Hospital, Reading, MA, 3Massachusetts General Hospital Rheumatology Unit, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA
Background/Purpose: IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a systemic autoimmune fibroinflammatory disease capable of affecting most organ systems. Large-vessel vasculitis is a well-described manifestation of the disease. However, coronary artery involvement, while rarely reported, is not well described. We aimed to characterize coronary involvement in 13 patients with IgG4-RD, the largest single-center experience with this manifestation reported to date.
Methods: Patients with coronary involvement of IgG4-RD were identified from our IgG4-RD cohort (n=359). Cases were defined as having coronary involvement if there was wall thickening or enhancement, periarterial soft tissue encasement, or aneurysm involving a coronary artery. Cases with only calcification or luminal stenosis but no other abnormalities were not considered to have coronary involvement. We extracted details regarding patients' diagnoses and characteristics of coronary involvement through manual chart review.
Results: Thirteen patients had IgG4-RD with coronary involvement. All were male, and median age at diagnosis of coronary involvement was 61 years (range 46-75, IQR 55-69) years. Timing of symptom onset could not be determined in 3 patients; in the remaining 10, median disease duration at diagnosis of coronary involvement was 11 years (IQR 8.3-15.5). Coronary involvement was identified incidentally (2/13), during workup or monitoring of IgG4-RD (7/13), or during workup of cardiac symptomatology (4/13). All patients had elevated serum IgG4 concentrations (median 955.4 [510-1568.3] mg/dL, range 235.2-1980, normal < 86.4 mg/dL), and they had a mean of 4.8 (1.9) organs involved. Concurrent large-vessel involvement was observed in 9/13 cases. Representative histology from a carotid artery is shown in Figure 1. Coronary artery aneurysms were present in 8/13, and these often met criteria for "giant" aneurysms. The largest measured 5.0 cm in diameter. Other abnormalities were periarterial soft tissue encasement (6/13), wall thickening or enhancement (8/13), calcification (9/13), and stenosis (9/13) (Figure 2). Advanced imaging demonstrated that both arteritis and periarteritis could occur (Figure 3). Complications included myocardial infarction (5/13), mural thrombus (5/13), and ischemic cardiomyopathy (2/13); percutaneous coronary intervention and coronary artery bypass grafting were performed in 2 patients each.
Conclusion: Coronary arteritis and periarteritis are manifestations of IgG4-RD, particularly in males with highly-elevated serum IgG4 concentrations and multiorgan disease. Patients are also likely asymptomatic for years, yet severe complications can occur. Our cohort likely underestimates the prevalence of coronary involvement, as patients did not routinely undergo coronary imaging.
<img src=https://www.abstractscorecard.com/uploads/Tasks/upload/17574/QHOPTGBB-1291572-1-ANY.jpg width=440 height=328.677640096172 border=0 style=border-style: none;>
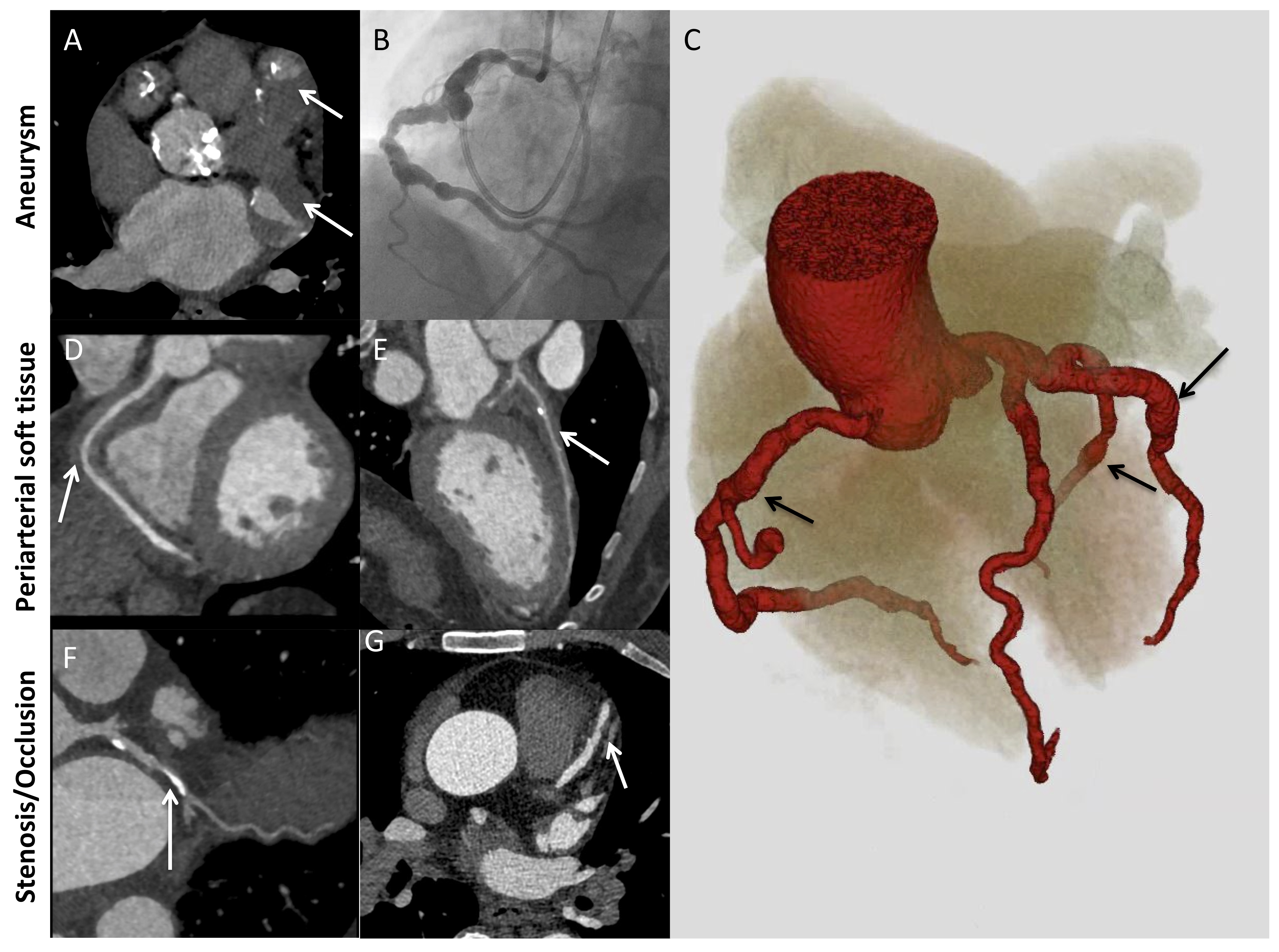 Figure 2. Major patterns of coronary artery involvement in IgG4-related disease. Images include axial CT (A), left heart catheterization (B), 3D volume-gated reconstruction of CTA (C), and curved planar reformatting of coronary CTA (D-G). Findings include fusiform aneurysmal dilatation (A-C) with mural thrombi (A, arrows), ectasia (C) periarterial soft tissue (D, E; arrows), and stenosis (F, G; arrows). Panel C demonstrates ectasia of the entire coronary tree with focal fusiform aneurysmal dilatations (arrows).
Figure 2. Major patterns of coronary artery involvement in IgG4-related disease. Images include axial CT (A), left heart catheterization (B), 3D volume-gated reconstruction of CTA (C), and curved planar reformatting of coronary CTA (D-G). Findings include fusiform aneurysmal dilatation (A-C) with mural thrombi (A, arrows), ectasia (C) periarterial soft tissue (D, E; arrows), and stenosis (F, G; arrows). Panel C demonstrates ectasia of the entire coronary tree with focal fusiform aneurysmal dilatations (arrows).
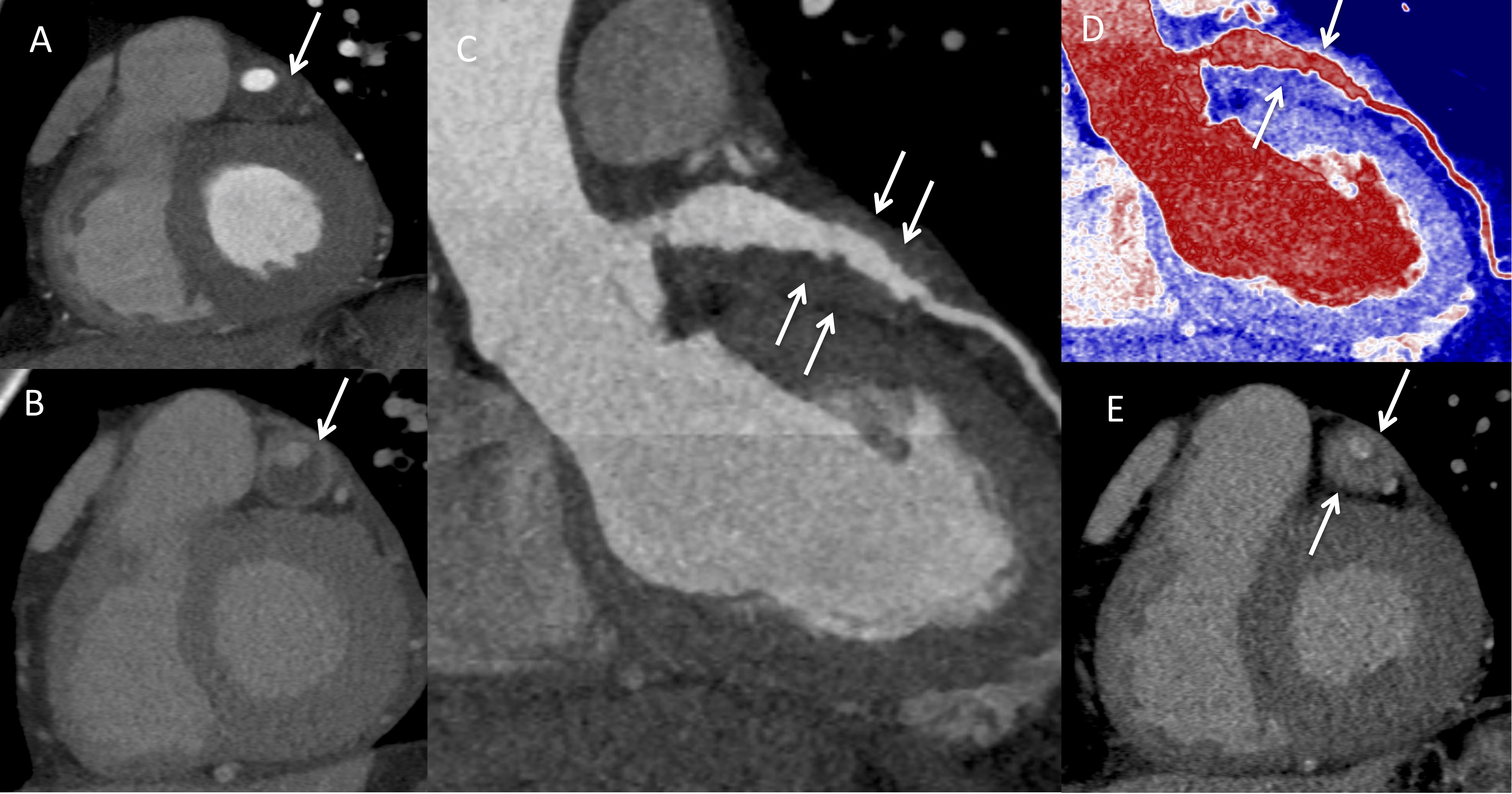 Figure 3. Arteritis and periarteritis. A) Coronary computed tomography (CTA) in the short-axis view demonstrating the left anterior descending artery (LAD) aneurysm (arrow). B) Delayed contrast-enhanced CT showing enhancement of the aneurysmal LAD wall consistent with arteritis (arrow). C) LAD curved planar reformatted (CPR) and D) Pseudo colorized image of the LAD CPR image showing the soft tissue thickening around the LAD (arrows). E) Delayed phase image in short axis showing enhancement of the soft tissue thickening consistent with periarteritis (arrows).
Figure 3. Arteritis and periarteritis. A) Coronary computed tomography (CTA) in the short-axis view demonstrating the left anterior descending artery (LAD) aneurysm (arrow). B) Delayed contrast-enhanced CT showing enhancement of the aneurysmal LAD wall consistent with arteritis (arrow). C) LAD curved planar reformatted (CPR) and D) Pseudo colorized image of the LAD CPR image showing the soft tissue thickening around the LAD (arrows). E) Delayed phase image in short axis showing enhancement of the soft tissue thickening consistent with periarteritis (arrows).
Disclosures: G. Katz, None; s. hedgire, None; J. Stone, Cook Medical; S. Perez-Espina, None; A. Fernandes, None; C. Perugino, None; Z. Wallace, Sanofi, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), Zenas Biopharma, Horizon, Shionogi; J. Stone, Horizon Theraputics, Sanofi, Amgen, Argenx, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), Chemocentryx, Kyverna, Novartis, Palleon Pharmaceuticals, PPD, Q32, Star Therapeutics, Roche, Mirabio, Spruce Biosciences, Steritas, Zenas.
Background/Purpose: IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a systemic autoimmune fibroinflammatory disease capable of affecting most organ systems. Large-vessel vasculitis is a well-described manifestation of the disease. However, coronary artery involvement, while rarely reported, is not well described. We aimed to characterize coronary involvement in 13 patients with IgG4-RD, the largest single-center experience with this manifestation reported to date.
Methods: Patients with coronary involvement of IgG4-RD were identified from our IgG4-RD cohort (n=359). Cases were defined as having coronary involvement if there was wall thickening or enhancement, periarterial soft tissue encasement, or aneurysm involving a coronary artery. Cases with only calcification or luminal stenosis but no other abnormalities were not considered to have coronary involvement. We extracted details regarding patients' diagnoses and characteristics of coronary involvement through manual chart review.
Results: Thirteen patients had IgG4-RD with coronary involvement. All were male, and median age at diagnosis of coronary involvement was 61 years (range 46-75, IQR 55-69) years. Timing of symptom onset could not be determined in 3 patients; in the remaining 10, median disease duration at diagnosis of coronary involvement was 11 years (IQR 8.3-15.5). Coronary involvement was identified incidentally (2/13), during workup or monitoring of IgG4-RD (7/13), or during workup of cardiac symptomatology (4/13). All patients had elevated serum IgG4 concentrations (median 955.4 [510-1568.3] mg/dL, range 235.2-1980, normal < 86.4 mg/dL), and they had a mean of 4.8 (1.9) organs involved. Concurrent large-vessel involvement was observed in 9/13 cases. Representative histology from a carotid artery is shown in Figure 1. Coronary artery aneurysms were present in 8/13, and these often met criteria for "giant" aneurysms. The largest measured 5.0 cm in diameter. Other abnormalities were periarterial soft tissue encasement (6/13), wall thickening or enhancement (8/13), calcification (9/13), and stenosis (9/13) (Figure 2). Advanced imaging demonstrated that both arteritis and periarteritis could occur (Figure 3). Complications included myocardial infarction (5/13), mural thrombus (5/13), and ischemic cardiomyopathy (2/13); percutaneous coronary intervention and coronary artery bypass grafting were performed in 2 patients each.
Conclusion: Coronary arteritis and periarteritis are manifestations of IgG4-RD, particularly in males with highly-elevated serum IgG4 concentrations and multiorgan disease. Patients are also likely asymptomatic for years, yet severe complications can occur. Our cohort likely underestimates the prevalence of coronary involvement, as patients did not routinely undergo coronary imaging.
<img src=https://www.abstractscorecard.com/uploads/Tasks/upload/17574/QHOPTGBB-1291572-1-ANY.jpg width=440 height=328.677640096172 border=0 style=border-style: none;>
Figure 1. Histopathology. Carotid artery biopsy at A) 20x magnification and B) 400x magnification showing dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate with >200 IgG4+ cells/high-powered field. C) CD138 stain and D) IgG4 stain demonstrate that 56% of CD138+ cells are IgG4+.
 Figure 2. Major patterns of coronary artery involvement in IgG4-related disease. Images include axial CT (A), left heart catheterization (B), 3D volume-gated reconstruction of CTA (C), and curved planar reformatting of coronary CTA (D-G). Findings include fusiform aneurysmal dilatation (A-C) with mural thrombi (A, arrows), ectasia (C) periarterial soft tissue (D, E; arrows), and stenosis (F, G; arrows). Panel C demonstrates ectasia of the entire coronary tree with focal fusiform aneurysmal dilatations (arrows).
Figure 2. Major patterns of coronary artery involvement in IgG4-related disease. Images include axial CT (A), left heart catheterization (B), 3D volume-gated reconstruction of CTA (C), and curved planar reformatting of coronary CTA (D-G). Findings include fusiform aneurysmal dilatation (A-C) with mural thrombi (A, arrows), ectasia (C) periarterial soft tissue (D, E; arrows), and stenosis (F, G; arrows). Panel C demonstrates ectasia of the entire coronary tree with focal fusiform aneurysmal dilatations (arrows).  Figure 3. Arteritis and periarteritis. A) Coronary computed tomography (CTA) in the short-axis view demonstrating the left anterior descending artery (LAD) aneurysm (arrow). B) Delayed contrast-enhanced CT showing enhancement of the aneurysmal LAD wall consistent with arteritis (arrow). C) LAD curved planar reformatted (CPR) and D) Pseudo colorized image of the LAD CPR image showing the soft tissue thickening around the LAD (arrows). E) Delayed phase image in short axis showing enhancement of the soft tissue thickening consistent with periarteritis (arrows).
Figure 3. Arteritis and periarteritis. A) Coronary computed tomography (CTA) in the short-axis view demonstrating the left anterior descending artery (LAD) aneurysm (arrow). B) Delayed contrast-enhanced CT showing enhancement of the aneurysmal LAD wall consistent with arteritis (arrow). C) LAD curved planar reformatted (CPR) and D) Pseudo colorized image of the LAD CPR image showing the soft tissue thickening around the LAD (arrows). E) Delayed phase image in short axis showing enhancement of the soft tissue thickening consistent with periarteritis (arrows).Disclosures: G. Katz, None; s. hedgire, None; J. Stone, Cook Medical; S. Perez-Espina, None; A. Fernandes, None; C. Perugino, None; Z. Wallace, Sanofi, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), Zenas Biopharma, Horizon, Shionogi; J. Stone, Horizon Theraputics, Sanofi, Amgen, Argenx, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), Chemocentryx, Kyverna, Novartis, Palleon Pharmaceuticals, PPD, Q32, Star Therapeutics, Roche, Mirabio, Spruce Biosciences, Steritas, Zenas.

