Back
Poster Session D
Crystal arthropathies
Session: (1787–1829) Metabolic and Crystal Arthropathies – Basic and Clinical Science Poster
1808: Assessing the Role of the NLRP3 Inflammasome in Driving Inflammation in Affected Joints of Patients with Inter-critical Gout
Monday, November 14, 2022
1:00 PM – 3:00 PM Eastern Time
Location: Virtual Poster Hall
.png)
Swamy Venuturupalli, MD
Cedars-Sinai Medical Center
Beverly Hills, CA, United States
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Swamy Venuturupalli1, Ami Ben-artzi2, Tasmia Amjad3, Amit Kumar4, Nikhil Davuluri3, Timothy Chu3, Umair Khan3, Diego Parra3, Natalie Fortune3 and Caroline Jefferies1, 1Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA, 2Ami Ben-Artzi, MD Inc., Beverly Hills, CA, 3Attune Health, Beverly Hills, CA, 4Attune Health, Beverly Hils, CA
Background/Purpose: Percutaneous ultrasound-guided needle synovial biopsies can now be performed at the bedside. To date, no synovial biopsy studies have been conducted in gout patients. Urate crystals drive IL-1β production and associated inflammation in affected joints via activating the NLRP3 inflammasome. The aim of this study was to assess gout patients during the inter-critical period to assess the role of the NLRP3 inflammasome in driving subclinical chronic inflammation.
Methods: We collected blood and synovial biopsies from four male patients of joints that had prior but not current gout flares. Histopathology and enzymatic digestion for downstream analysis by flow cytometry and qPCR were performed. Whole blood RNA was analyzed by qPCR while peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were isolated for flow cytometry analysis. CASPASE 1 (CASP1) activity was measured in samples. Serum from healthy matched controls and synovial biopsy tissue collected previously from Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) patients was used as controls.
Results: In whole blood, we found that IL1B mRNA levels but not TNFα levels were significantly increased in gout patients compared to RA patients, suggesting that in the inter-critical period, systemic levels of inflammatory cytokines are elevated (fig 1). We also observed increased expression of IL1B and CASP1, although not statistically significant, in gout patients compared to healthy controls (fig 1, left hand panel). In keeping with increased IL1B in whole blood samples, PBMCs from gout patients tended to have increased CASP1 activity at baseline (figure 2). Importantly, CASP1 expression was found to be elevated in gout synovial biopsies compared to RA biopsies (fig 3A). CASP1 activity was increased in CD45- stromal cells from gout patients compared to RA controls at baseline (n=2, figure 3B). However, whilst LPS induced CASP1 activation in CD45- stromal cells, CD3+ T cells and CD3-CD14- immune cells from gout biopsies (figure 3c), insufficient cell numbers were obtained to compare stimulation in RA samples (figure 3C).
Conclusion: In synovial biopsies of gout patients during the inter-critical period, we observed increased levels of CASP1 mRNA, suggesting CASP1 activity may be higher. We also observed higher CASP1 and IL1B expression in blood from patients with inter-critical gout compared to blood from healthy controls. PBMCs from gout patients in the inter-critical phase also appeared to have enhanced CASP1 activity. Although underpowered, our preliminary data suggests that CASP1 activity is indeed increased in the joints of patients with inter-critical gout compared to RA patients, which is a novel finding.
.jpg) Figure 1: RNA was extracted from whole blood samples from patients with inter-critical gout (n=4), health controls (HC) (n=4) and patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) (n=6). Levels of gene expression where determined by qPCR and expression of genes in gout patients was relative to HC and RA patient levels. Data is pooled data from patients and HC samples. Statistical significance was determined by Student t test, with p < 0.05 being considered significant.
Figure 1: RNA was extracted from whole blood samples from patients with inter-critical gout (n=4), health controls (HC) (n=4) and patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) (n=6). Levels of gene expression where determined by qPCR and expression of genes in gout patients was relative to HC and RA patient levels. Data is pooled data from patients and HC samples. Statistical significance was determined by Student t test, with p < 0.05 being considered significant.
** = p < 0.001
***=p < 0.0001
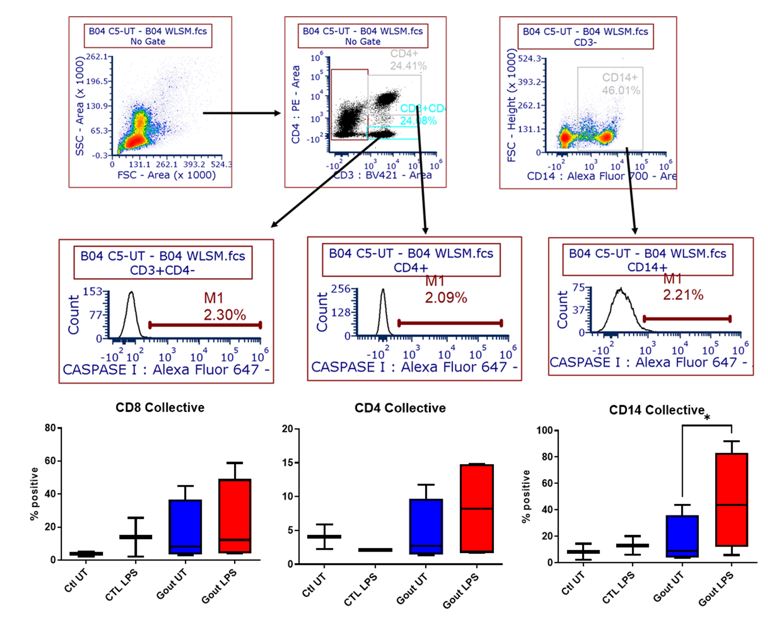 Figure 2: PBMCs from gout patients (n=4) were stained for surface markers (CD45, CD4, CD14) and caspase activity measured following LPS and nigercin priming. Representative schematic showing gating strategy and LPS-induced CASPASE-1 activity in CD4+, CD8+ and CD14+ cells (n=4), lower panel. Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA, with p < 0.05 considered significant.
Figure 2: PBMCs from gout patients (n=4) were stained for surface markers (CD45, CD4, CD14) and caspase activity measured following LPS and nigercin priming. Representative schematic showing gating strategy and LPS-induced CASPASE-1 activity in CD4+, CD8+ and CD14+ cells (n=4), lower panel. Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA, with p < 0.05 considered significant.
.jpg) Figure 3: (A) CASPASE-1 expression was measured in synovial biopsies from RA (n=6) and gout patients (n=4) by qPCR; (B-C) synovial biopsies from gout patients (n=4) were digested, stained for surface markers (CD45, CD4, CD14) and caspase activity measured. (B) Caspase activity compared in CD45-stromal cells from gout (n=4) and RA (n=2) synovial biopsies; (C) Representative schematic showing gating strategy and LPS-induced caspase-1 activity (red line) in the CD45- stromal cells, CD3+ T cells, CD14+ monocytes and CD3-CD14-immune populations.
Figure 3: (A) CASPASE-1 expression was measured in synovial biopsies from RA (n=6) and gout patients (n=4) by qPCR; (B-C) synovial biopsies from gout patients (n=4) were digested, stained for surface markers (CD45, CD4, CD14) and caspase activity measured. (B) Caspase activity compared in CD45-stromal cells from gout (n=4) and RA (n=2) synovial biopsies; (C) Representative schematic showing gating strategy and LPS-induced caspase-1 activity (red line) in the CD45- stromal cells, CD3+ T cells, CD14+ monocytes and CD3-CD14-immune populations.
Disclosures: S. Venuturupalli, Horizon Pharma USA, Inc., Kezar Life Sciences, Inc., Mallinckrodt, Inc., Navidea Biopharmaceuticals, Inc., Pfizer (Current), Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), Argenx, Janssen; A. Ben-artzi, None; T. Amjad, None; A. Kumar, None; N. Davuluri, None; T. Chu, None; U. Khan, None; D. Parra, None; N. Fortune, None; C. Jefferies, None.
Background/Purpose: Percutaneous ultrasound-guided needle synovial biopsies can now be performed at the bedside. To date, no synovial biopsy studies have been conducted in gout patients. Urate crystals drive IL-1β production and associated inflammation in affected joints via activating the NLRP3 inflammasome. The aim of this study was to assess gout patients during the inter-critical period to assess the role of the NLRP3 inflammasome in driving subclinical chronic inflammation.
Methods: We collected blood and synovial biopsies from four male patients of joints that had prior but not current gout flares. Histopathology and enzymatic digestion for downstream analysis by flow cytometry and qPCR were performed. Whole blood RNA was analyzed by qPCR while peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were isolated for flow cytometry analysis. CASPASE 1 (CASP1) activity was measured in samples. Serum from healthy matched controls and synovial biopsy tissue collected previously from Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) patients was used as controls.
Results: In whole blood, we found that IL1B mRNA levels but not TNFα levels were significantly increased in gout patients compared to RA patients, suggesting that in the inter-critical period, systemic levels of inflammatory cytokines are elevated (fig 1). We also observed increased expression of IL1B and CASP1, although not statistically significant, in gout patients compared to healthy controls (fig 1, left hand panel). In keeping with increased IL1B in whole blood samples, PBMCs from gout patients tended to have increased CASP1 activity at baseline (figure 2). Importantly, CASP1 expression was found to be elevated in gout synovial biopsies compared to RA biopsies (fig 3A). CASP1 activity was increased in CD45- stromal cells from gout patients compared to RA controls at baseline (n=2, figure 3B). However, whilst LPS induced CASP1 activation in CD45- stromal cells, CD3+ T cells and CD3-CD14- immune cells from gout biopsies (figure 3c), insufficient cell numbers were obtained to compare stimulation in RA samples (figure 3C).
Conclusion: In synovial biopsies of gout patients during the inter-critical period, we observed increased levels of CASP1 mRNA, suggesting CASP1 activity may be higher. We also observed higher CASP1 and IL1B expression in blood from patients with inter-critical gout compared to blood from healthy controls. PBMCs from gout patients in the inter-critical phase also appeared to have enhanced CASP1 activity. Although underpowered, our preliminary data suggests that CASP1 activity is indeed increased in the joints of patients with inter-critical gout compared to RA patients, which is a novel finding.
.jpg) Figure 1: RNA was extracted from whole blood samples from patients with inter-critical gout (n=4), health controls (HC) (n=4) and patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) (n=6). Levels of gene expression where determined by qPCR and expression of genes in gout patients was relative to HC and RA patient levels. Data is pooled data from patients and HC samples. Statistical significance was determined by Student t test, with p < 0.05 being considered significant.
Figure 1: RNA was extracted from whole blood samples from patients with inter-critical gout (n=4), health controls (HC) (n=4) and patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) (n=6). Levels of gene expression where determined by qPCR and expression of genes in gout patients was relative to HC and RA patient levels. Data is pooled data from patients and HC samples. Statistical significance was determined by Student t test, with p < 0.05 being considered significant. ** = p < 0.001
***=p < 0.0001
 Figure 2: PBMCs from gout patients (n=4) were stained for surface markers (CD45, CD4, CD14) and caspase activity measured following LPS and nigercin priming. Representative schematic showing gating strategy and LPS-induced CASPASE-1 activity in CD4+, CD8+ and CD14+ cells (n=4), lower panel. Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA, with p < 0.05 considered significant.
Figure 2: PBMCs from gout patients (n=4) were stained for surface markers (CD45, CD4, CD14) and caspase activity measured following LPS and nigercin priming. Representative schematic showing gating strategy and LPS-induced CASPASE-1 activity in CD4+, CD8+ and CD14+ cells (n=4), lower panel. Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA, with p < 0.05 considered significant. .jpg) Figure 3: (A) CASPASE-1 expression was measured in synovial biopsies from RA (n=6) and gout patients (n=4) by qPCR; (B-C) synovial biopsies from gout patients (n=4) were digested, stained for surface markers (CD45, CD4, CD14) and caspase activity measured. (B) Caspase activity compared in CD45-stromal cells from gout (n=4) and RA (n=2) synovial biopsies; (C) Representative schematic showing gating strategy and LPS-induced caspase-1 activity (red line) in the CD45- stromal cells, CD3+ T cells, CD14+ monocytes and CD3-CD14-immune populations.
Figure 3: (A) CASPASE-1 expression was measured in synovial biopsies from RA (n=6) and gout patients (n=4) by qPCR; (B-C) synovial biopsies from gout patients (n=4) were digested, stained for surface markers (CD45, CD4, CD14) and caspase activity measured. (B) Caspase activity compared in CD45-stromal cells from gout (n=4) and RA (n=2) synovial biopsies; (C) Representative schematic showing gating strategy and LPS-induced caspase-1 activity (red line) in the CD45- stromal cells, CD3+ T cells, CD14+ monocytes and CD3-CD14-immune populations.Disclosures: S. Venuturupalli, Horizon Pharma USA, Inc., Kezar Life Sciences, Inc., Mallinckrodt, Inc., Navidea Biopharmaceuticals, Inc., Pfizer (Current), Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), Argenx, Janssen; A. Ben-artzi, None; T. Amjad, None; A. Kumar, None; N. Davuluri, None; T. Chu, None; U. Khan, None; D. Parra, None; N. Fortune, None; C. Jefferies, None.

