Back
Abstract Session
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
Session: Abstracts: SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes II: Complications (1591–1596)
1593: Epidemiology and Outcomes of Infection-related Hospitalizations in Young Adults with SLE: Data from National Inpatient Sample
Sunday, November 13, 2022
3:30 PM – 3:40 PM Eastern Time
Location: Room 204
- RD
Rashmi Dhital, MD
UC San Diego
San Diego, CA, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Rashmi Dhital1, Monica Guma2, Dilli Poudel3 and Kenneth Kalunian4, 1UC San Diego, San Diego, CA, 2UCSD, La Jolla, CA, 3Indiana Regional Medical Center, Indiana, PA, 4University of California San Diego, La Jolla, CA
Background/Purpose: Infection is the leading cause of hospitalization and mortality in SLE. Care of young adults (YA) with SLE is particularly challenging, with higher mortality and disease activity noted in the immediate post-transition period from pediatric to adult rheumatology. Epidemiological studies focused on serious infection-related hospitalizations (SIH) in young adults with SLE (YA-SLE) are rare. In this study, we aimed to compare the infection rates, trends, patient characteristics, and outcomes for SIH by age categories in SLE, with a focus on young adults, using the largest publicly available all-payer inpatient database in the US, National Inpatient Sample (NIS).
Methods: We used NIS data from the years 2000-2019 to study the trends of SIH. The primary outcome was the rates of SIH in YA-SLE as compared to late adults with SLE (LA-SLE) and to young adults without SLE (YA-no SLE). STATA and Joinpoint Regression Program were used for analysis, and yearly changes in trends were calculated as annual percent change (APC).
Results: From 2010-2019, we identified a weighted national estimate of 1,732,467 hospitalizations with SLE in patients ≥13 years age. Of these, adolescents (13-17 years), young (18-24 years), late (25-49 years), and older adults (≥50 years) comprised on 9,990 (0.6%), 72,968 (4.2%), 647,438 (37.4%) and 1,002,072 (57.8%) hospitalizations, respectively Rates of SIH in YA-SLE were similar to LA-SLE (15% versus 14.7%, p=0.32), and considerably higher than YA- no SLE (15% versus 4.2%, p< 0.001) (Figure 1). Among SLE adults, septicemia, followed by pneumonia was the commonest primary diagnosis, accounting for ~ 45-50% and 20-25% of SIH, respectively. Significantly higher YA-SLE compared to LA-SLE and YA-no SLE comprised of non-white races, belonged to the lowest income quartile, and had Medicaid as their primary payer. The mean length of stay (LOS) and cost for YA-SLE were similar to LA-SLE and significantly higher than YA-no SLE (Table 1). In the 20-year period between 2000-2019, increasing trends of SIH in YA-SLE (APC 1.90, p< 0.05) LA-SLE (APC 2.62, p< 0.05) and YA- no SLE (APC 3.98, p< 0.05) (Figure 2), were all driven by increase in septicemia.
Conclusion: NIS is nationally representative and provides a readily available source of "real-world" health care data on a large population. Our results show that although young adults comprised a notably lower proportion of overall SLE hospitalizations compared to late adults, they have similar rates of SIH, and similar LOS and cost. Compared to late SLE adults, young SLE adults with SIH comprised of higher proportions of racial and socioeconomic minorities. Septicemia was the driver of the increasing trend of SIH.
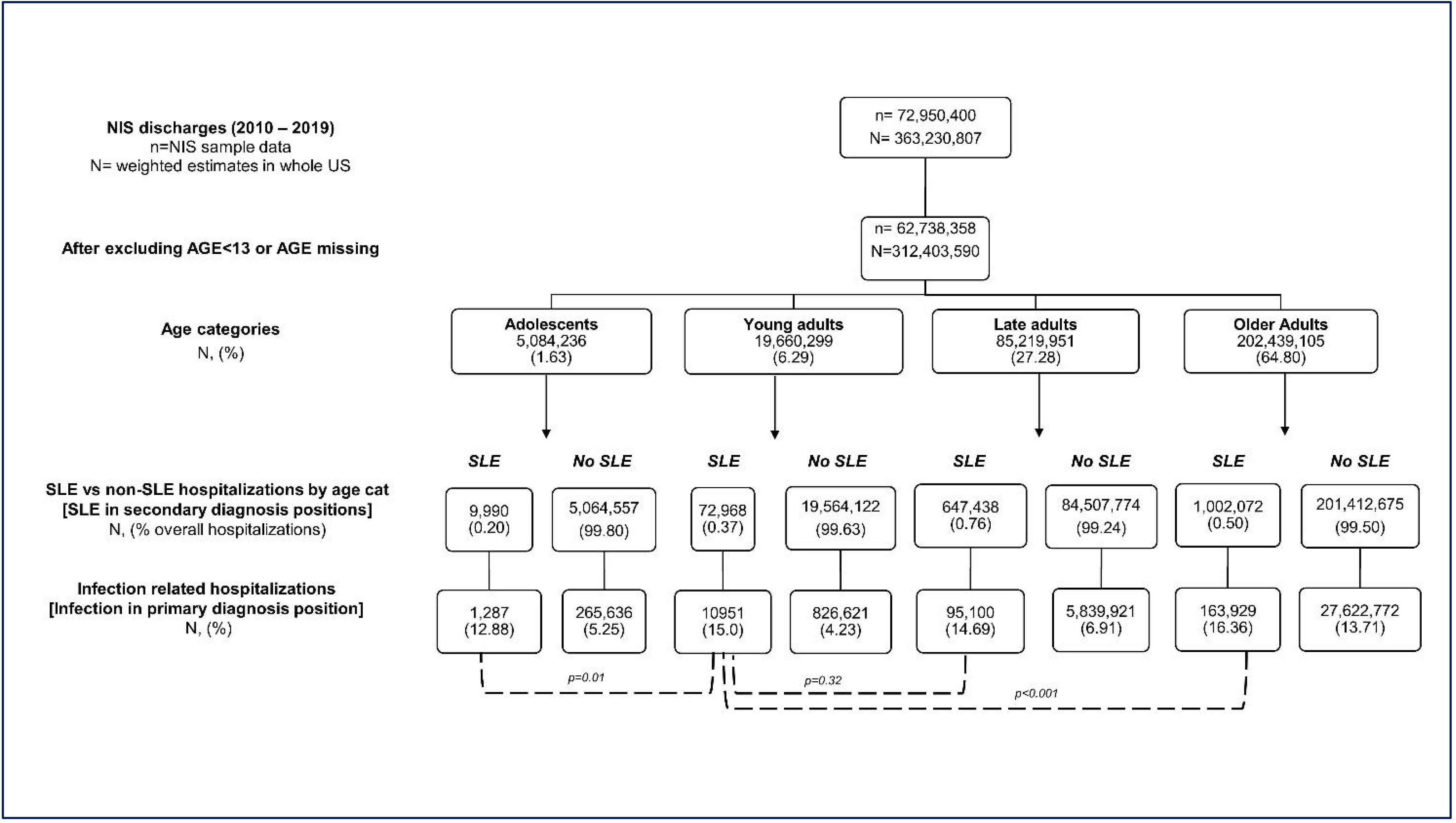 Figure 1: Comparison of rates of serious infection-related hospitalizations (SIH) among different age categories of SLE and non-SLE patients. Adolescents (13-17), young adults (18-24), late adults (25-49), and older adults (≥50 years)
Figure 1: Comparison of rates of serious infection-related hospitalizations (SIH) among different age categories of SLE and non-SLE patients. Adolescents (13-17), young adults (18-24), late adults (25-49), and older adults (≥50 years)
.jpg) Table 1: Baseline characteristics and hospitalization outcomes of serious infection-related hospitalizations (SIH) among young adults and late adults with SLE
Table 1: Baseline characteristics and hospitalization outcomes of serious infection-related hospitalizations (SIH) among young adults and late adults with SLE
.jpg) Figure 2: Trends of serious infection-related hospitalizations (SIH) among different age categories of SLE. Ad: Adolescents (13-17), YA: young adults (18-24), LA: late adults (25-49), and OA: older adults (≥50 years).
Figure 2: Trends of serious infection-related hospitalizations (SIH) among different age categories of SLE. Ad: Adolescents (13-17), YA: young adults (18-24), LA: late adults (25-49), and OA: older adults (≥50 years).
The rate of change in annual trend, calculated using Joinpoint regression software, is expressed as Annual Percent Change (APC), *p < 0.05
Disclosures: R. Dhital, None; M. Guma, Pfizer, Novartis, Gilead, Sonoma Bio, Genentech; D. Poudel, None; K. Kalunian, AbbVie/Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Aurinia, Biogen, Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS), Eli Lilly, Equillium, Genentech, Gilead, Janssen, Roche, Lupus Research Alliance, Pfizer, Sanford Consortium, Viela, Nektar.
Background/Purpose: Infection is the leading cause of hospitalization and mortality in SLE. Care of young adults (YA) with SLE is particularly challenging, with higher mortality and disease activity noted in the immediate post-transition period from pediatric to adult rheumatology. Epidemiological studies focused on serious infection-related hospitalizations (SIH) in young adults with SLE (YA-SLE) are rare. In this study, we aimed to compare the infection rates, trends, patient characteristics, and outcomes for SIH by age categories in SLE, with a focus on young adults, using the largest publicly available all-payer inpatient database in the US, National Inpatient Sample (NIS).
Methods: We used NIS data from the years 2000-2019 to study the trends of SIH. The primary outcome was the rates of SIH in YA-SLE as compared to late adults with SLE (LA-SLE) and to young adults without SLE (YA-no SLE). STATA and Joinpoint Regression Program were used for analysis, and yearly changes in trends were calculated as annual percent change (APC).
Results: From 2010-2019, we identified a weighted national estimate of 1,732,467 hospitalizations with SLE in patients ≥13 years age. Of these, adolescents (13-17 years), young (18-24 years), late (25-49 years), and older adults (≥50 years) comprised on 9,990 (0.6%), 72,968 (4.2%), 647,438 (37.4%) and 1,002,072 (57.8%) hospitalizations, respectively Rates of SIH in YA-SLE were similar to LA-SLE (15% versus 14.7%, p=0.32), and considerably higher than YA- no SLE (15% versus 4.2%, p< 0.001) (Figure 1). Among SLE adults, septicemia, followed by pneumonia was the commonest primary diagnosis, accounting for ~ 45-50% and 20-25% of SIH, respectively. Significantly higher YA-SLE compared to LA-SLE and YA-no SLE comprised of non-white races, belonged to the lowest income quartile, and had Medicaid as their primary payer. The mean length of stay (LOS) and cost for YA-SLE were similar to LA-SLE and significantly higher than YA-no SLE (Table 1). In the 20-year period between 2000-2019, increasing trends of SIH in YA-SLE (APC 1.90, p< 0.05) LA-SLE (APC 2.62, p< 0.05) and YA- no SLE (APC 3.98, p< 0.05) (Figure 2), were all driven by increase in septicemia.
Conclusion: NIS is nationally representative and provides a readily available source of "real-world" health care data on a large population. Our results show that although young adults comprised a notably lower proportion of overall SLE hospitalizations compared to late adults, they have similar rates of SIH, and similar LOS and cost. Compared to late SLE adults, young SLE adults with SIH comprised of higher proportions of racial and socioeconomic minorities. Septicemia was the driver of the increasing trend of SIH.
 Figure 1: Comparison of rates of serious infection-related hospitalizations (SIH) among different age categories of SLE and non-SLE patients. Adolescents (13-17), young adults (18-24), late adults (25-49), and older adults (≥50 years)
Figure 1: Comparison of rates of serious infection-related hospitalizations (SIH) among different age categories of SLE and non-SLE patients. Adolescents (13-17), young adults (18-24), late adults (25-49), and older adults (≥50 years).jpg) Table 1: Baseline characteristics and hospitalization outcomes of serious infection-related hospitalizations (SIH) among young adults and late adults with SLE
Table 1: Baseline characteristics and hospitalization outcomes of serious infection-related hospitalizations (SIH) among young adults and late adults with SLE.jpg) Figure 2: Trends of serious infection-related hospitalizations (SIH) among different age categories of SLE. Ad: Adolescents (13-17), YA: young adults (18-24), LA: late adults (25-49), and OA: older adults (≥50 years).
Figure 2: Trends of serious infection-related hospitalizations (SIH) among different age categories of SLE. Ad: Adolescents (13-17), YA: young adults (18-24), LA: late adults (25-49), and OA: older adults (≥50 years). The rate of change in annual trend, calculated using Joinpoint regression software, is expressed as Annual Percent Change (APC), *p < 0.05
Disclosures: R. Dhital, None; M. Guma, Pfizer, Novartis, Gilead, Sonoma Bio, Genentech; D. Poudel, None; K. Kalunian, AbbVie/Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Aurinia, Biogen, Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS), Eli Lilly, Equillium, Genentech, Gilead, Janssen, Roche, Lupus Research Alliance, Pfizer, Sanford Consortium, Viela, Nektar.

