Back
Abstract Session
Sjögren's syndrome
Session: Abstracts: Sjögren's Syndrome – Basic and Clinical Science (1625–1628)
1625: Single Cell and Spatial Transcriptomics Identifies Pathogenic Drivers of Sjogren’s Disease in Humans
Sunday, November 13, 2022
5:00 PM – 5:10 PM Eastern Time
Location: Room 204
- DW
Dr. Blake M. Warner, PhD, MPH, DDS
National Institutes of Health
Bethesda, MD, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Blake Warner1, Thomas Pranzatelli2, Paola Perez2, Daniel Martin2, Shyh-Ing Jang2, Kalie Dominick2, Eiko Yamada2, Kevin Byrd3, Quinn Easter4, A. Darise Farris5, Christopher Lessard5, Amanda Oliver6, Raquel Bartolome-Casado6, Zohreh Khavandgar1, Sarthak Gupta7, Sarah Teichmann6, Alan Baer8 and John Chiorini2, 1National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, 2NIDCR, Bethesda, MD, 3American Dental Association, Scientific Research Institute, Gaithersburg, MD, 4American Dental Association, Gaithersburg, MD, 5Oklahoma Medical Research Foundation, Oklahoma City, OK, 6Wellcome Sanger Institute, Cambridgeshire, United Kingdom, 7National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS), National Institutes of Health (NIH), Bethesda, MD, 8Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD
Background/Purpose: Sjogren's Disease(SjD) is a systemic autoimmune disease characterized by exocrine dysfunction. The pathogenesis is incompletely understood, but involves gene-environment interactions leading to infiltration of immune cells and autoimmunity. Immune-epithelial crosstalk and the mechanisms driving exocrine dysfunction remain ill-defined. High throughput transcriptional analyses have broadened our understanding the etiopathogenesis of SjD. However, 'bulk' approaches cannot uncouple disease-specific changes in cellularity and cell-state simultaneously and lack direct spatial context. We hypothesized that single cell(sc) and spatial transcriptomics(st) approaches can directly unravel the immunopathology of SjD in the salivary glands.
Methods: scRNAseq was performed on human minor salivary glands(MSG; SjD: n=12, HV: n=17) and paired peripheral blood mononuclear cells(PBMCs; SjD: n=8, HV: n=7) to assess cellular composition and transcriptional states. MSG(SjD: n=24; HV: n=24) were sectioned onto 10X Visium slides and sequenced. Cell2location was used to analyze altered cellularity and interactions from stRNAseq datasets. Utilization of signaling pathways in sc and st datasets was assessed across annotated pathways. MSG were also used for flow cytometry, HiPlex in situ hybridization, and immunohistochemistry as confirmation.
Results: scRNAseq of MSG, but not PBMCs, exhibited profound changes in cellularity and differentially expressed genes(DEG) in SjD(Figure 1). SjD MSG had more inflammatory cells(e.g., T cells, B cells, and antigen presenting cells[APC]; and loss of seromucous cells). In SjD, many cell types' DEG sets showed increased expression of MHC class I, B2M and HLA-B, and interferon (IFN) stimulated genes(e.g., ISG15). These phenomena were dependent on autoantibody positivity, but not focus score. In acinar cells, secretory markers(MUC7, AQP5) were significantly decreased. In T cell clusters(CD8, CD4), functional annotation analysis revealed marked activation of T cells including: 'positive regulation of the Type I IFN response', 'T cell receptor signaling', and 'response to IFNg signaling'. PMA/ionomycin stimulation of MSG lymphocytes showed that CD8+T-cells were significantly more cytotoxic than in HV(Figure 1). Profound cellularity-dependent architectural and transcriptional changes in the glands and disease-specific cell-cell interactions(e.g., T cells:APC, T cells:acinar cells) and altered cellular neighborhoods were identified using stRNAseq(Figure 2).
Conclusion: Multiomics single cell and spatially transcriptomic approaches disentangle the complex disease-dependent tissue disorganization, cellular compositional alterations, and transcriptional cellular states in the salivary glands of SjD patients. Our findings link loss of secretory cells and gland function, with the presence of cytotoxic CD8+T-cells. Further, these results emphasize the expression modules and spatial arrangement of immune cells, and their interactions, promoting tissue damage in the salivary glands. In summary, these data pinpoint pathogenic cell populations, and their interactions, that may be directly targetable for therapeutic intervention.
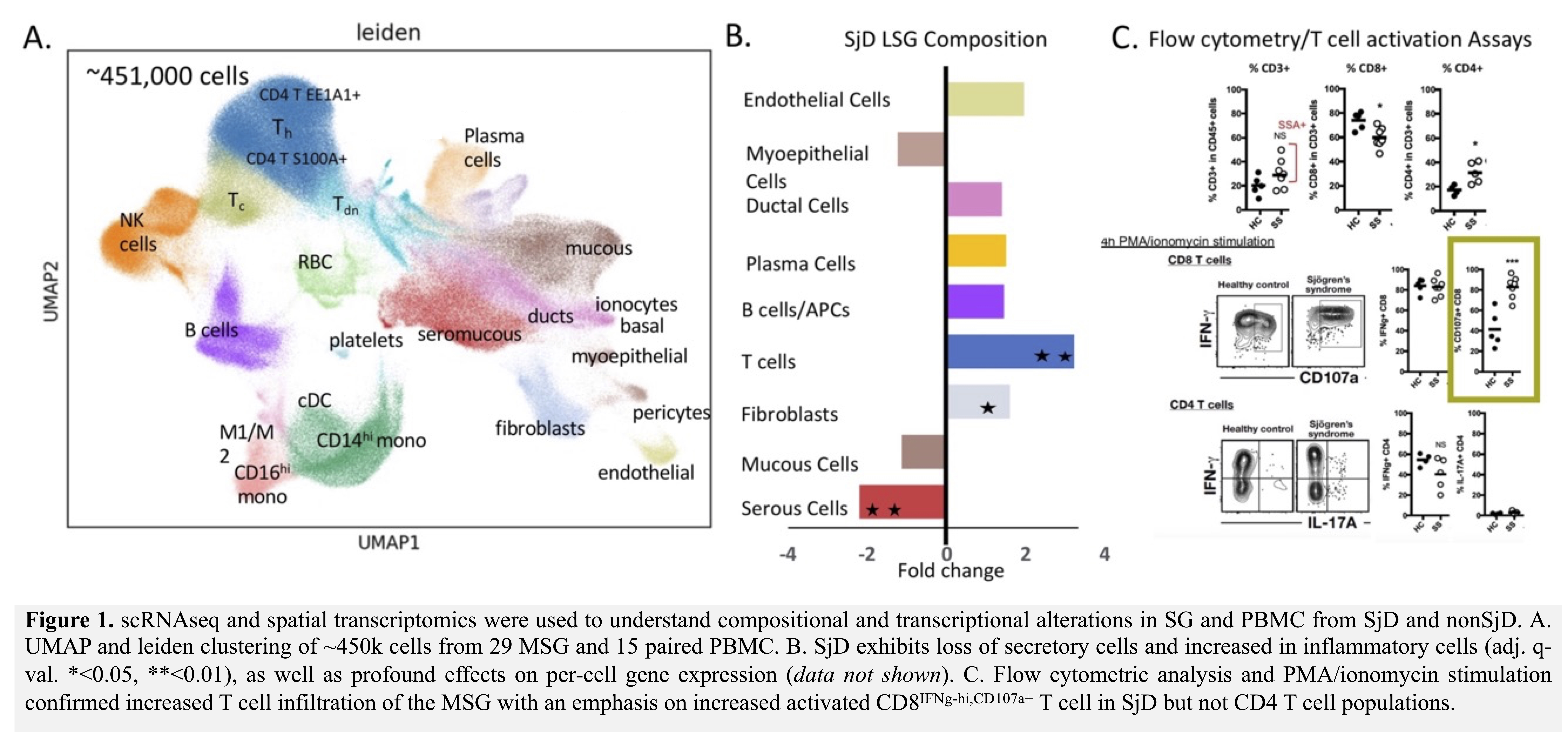 Figure 1. scRNAseq and spatial transcriptomics were used to understand compositional and transcriptional alterations in SG and PBMC from SjD and nonSjD. A. UMAP and leiden clustering of ~450k cells from 29 MSG and 15 paired PBMC. B. SjD exhibits loss of secretory cells and increased in inflammatory cells (adj. q-val. * < 0.05, ** < 0.01), as well as profound effects on per-cell gene expression (data not shown). C. Flow cytometric analysis and PMA/ionomycin stimulation confirmed increased T cell infiltration of the MSG with an emphasis on increased activated CD8IFNg-hi,CD107a+ T cell in SjD but not CD4 T cell populations.
Figure 1. scRNAseq and spatial transcriptomics were used to understand compositional and transcriptional alterations in SG and PBMC from SjD and nonSjD. A. UMAP and leiden clustering of ~450k cells from 29 MSG and 15 paired PBMC. B. SjD exhibits loss of secretory cells and increased in inflammatory cells (adj. q-val. * < 0.05, ** < 0.01), as well as profound effects on per-cell gene expression (data not shown). C. Flow cytometric analysis and PMA/ionomycin stimulation confirmed increased T cell infiltration of the MSG with an emphasis on increased activated CD8IFNg-hi,CD107a+ T cell in SjD but not CD4 T cell populations.
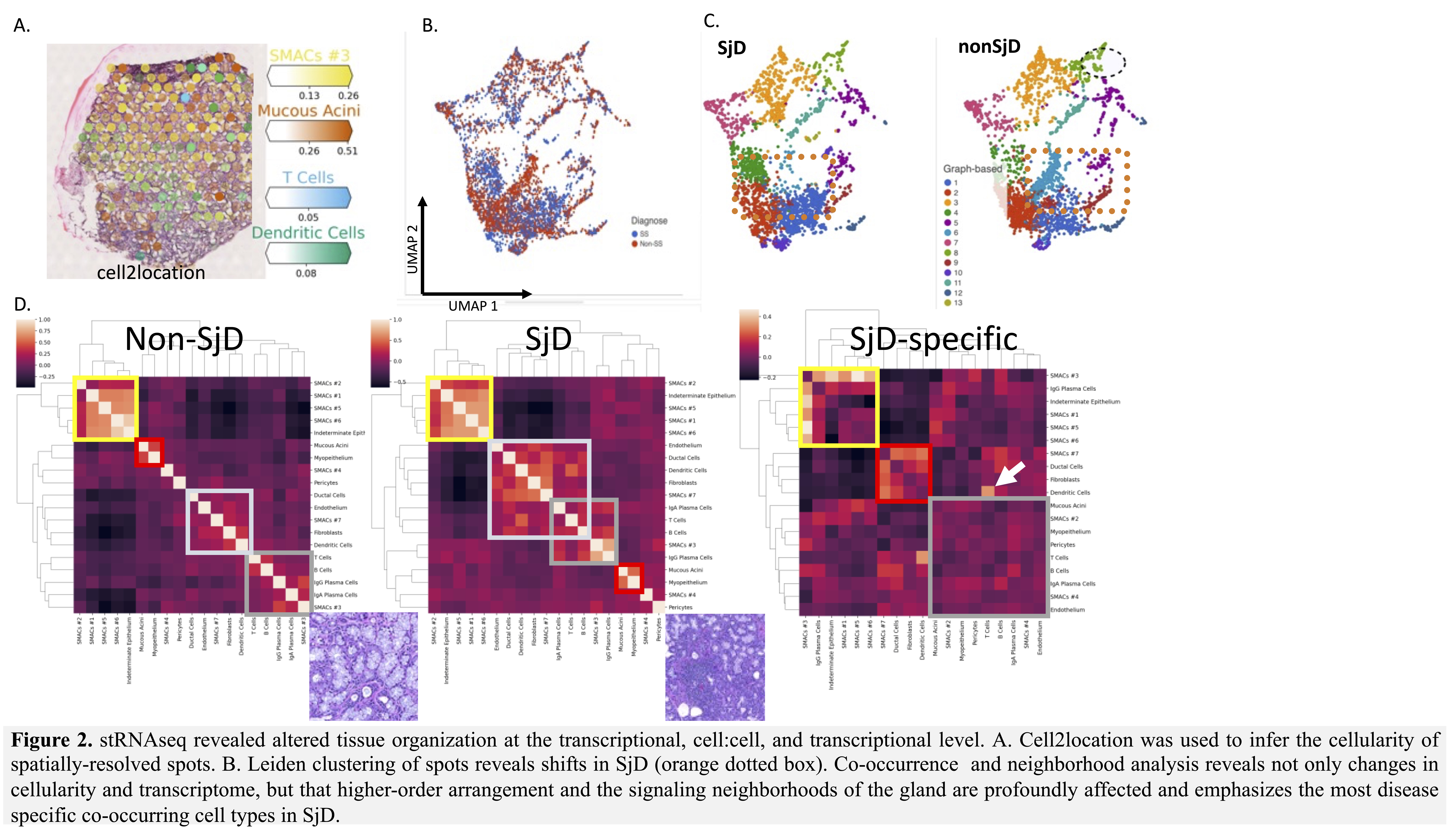 Figure 2. stRNAseq revealed altered tissue organization at the transcriptional, cell:cell, and transcriptional level. A. Cell2location was used to infer the cellularity of spatially-resolved spots. B. Leiden clustering of spots reveals shifts in SjD (orange dotted box). Co-occurrence and neighborhood analysis reveals not only changes in cellularity and transcriptome, but that higher-order arrangement and the signaling neighborhoods of the gland are profoundly affected and emphasizes the most disease specific co-occurring cell types in SjD.
Figure 2. stRNAseq revealed altered tissue organization at the transcriptional, cell:cell, and transcriptional level. A. Cell2location was used to infer the cellularity of spatially-resolved spots. B. Leiden clustering of spots reveals shifts in SjD (orange dotted box). Co-occurrence and neighborhood analysis reveals not only changes in cellularity and transcriptome, but that higher-order arrangement and the signaling neighborhoods of the gland are profoundly affected and emphasizes the most disease specific co-occurring cell types in SjD.
Disclosures: B. Warner, Pfizer, Astellas Bio; T. Pranzatelli, None; P. Perez, None; D. Martin, None; S. Jang, None; K. Dominick, None; E. Yamada, None; K. Byrd, None; Q. Easter, None; A. Farris, Janssen; C. Lessard, Janssen; A. Oliver, None; R. Bartolome-Casado, None; Z. Khavandgar, None; S. Gupta, None; S. Teichmann, None; A. Baer, None; J. Chiorini, None.
Background/Purpose: Sjogren's Disease(SjD) is a systemic autoimmune disease characterized by exocrine dysfunction. The pathogenesis is incompletely understood, but involves gene-environment interactions leading to infiltration of immune cells and autoimmunity. Immune-epithelial crosstalk and the mechanisms driving exocrine dysfunction remain ill-defined. High throughput transcriptional analyses have broadened our understanding the etiopathogenesis of SjD. However, 'bulk' approaches cannot uncouple disease-specific changes in cellularity and cell-state simultaneously and lack direct spatial context. We hypothesized that single cell(sc) and spatial transcriptomics(st) approaches can directly unravel the immunopathology of SjD in the salivary glands.
Methods: scRNAseq was performed on human minor salivary glands(MSG; SjD: n=12, HV: n=17) and paired peripheral blood mononuclear cells(PBMCs; SjD: n=8, HV: n=7) to assess cellular composition and transcriptional states. MSG(SjD: n=24; HV: n=24) were sectioned onto 10X Visium slides and sequenced. Cell2location was used to analyze altered cellularity and interactions from stRNAseq datasets. Utilization of signaling pathways in sc and st datasets was assessed across annotated pathways. MSG were also used for flow cytometry, HiPlex in situ hybridization, and immunohistochemistry as confirmation.
Results: scRNAseq of MSG, but not PBMCs, exhibited profound changes in cellularity and differentially expressed genes(DEG) in SjD(Figure 1). SjD MSG had more inflammatory cells(e.g., T cells, B cells, and antigen presenting cells[APC]; and loss of seromucous cells). In SjD, many cell types' DEG sets showed increased expression of MHC class I, B2M and HLA-B, and interferon (IFN) stimulated genes(e.g., ISG15). These phenomena were dependent on autoantibody positivity, but not focus score. In acinar cells, secretory markers(MUC7, AQP5) were significantly decreased. In T cell clusters(CD8, CD4), functional annotation analysis revealed marked activation of T cells including: 'positive regulation of the Type I IFN response', 'T cell receptor signaling', and 'response to IFNg signaling'. PMA/ionomycin stimulation of MSG lymphocytes showed that CD8+T-cells were significantly more cytotoxic than in HV(Figure 1). Profound cellularity-dependent architectural and transcriptional changes in the glands and disease-specific cell-cell interactions(e.g., T cells:APC, T cells:acinar cells) and altered cellular neighborhoods were identified using stRNAseq(Figure 2).
Conclusion: Multiomics single cell and spatially transcriptomic approaches disentangle the complex disease-dependent tissue disorganization, cellular compositional alterations, and transcriptional cellular states in the salivary glands of SjD patients. Our findings link loss of secretory cells and gland function, with the presence of cytotoxic CD8+T-cells. Further, these results emphasize the expression modules and spatial arrangement of immune cells, and their interactions, promoting tissue damage in the salivary glands. In summary, these data pinpoint pathogenic cell populations, and their interactions, that may be directly targetable for therapeutic intervention.
 Figure 1. scRNAseq and spatial transcriptomics were used to understand compositional and transcriptional alterations in SG and PBMC from SjD and nonSjD. A. UMAP and leiden clustering of ~450k cells from 29 MSG and 15 paired PBMC. B. SjD exhibits loss of secretory cells and increased in inflammatory cells (adj. q-val. * < 0.05, ** < 0.01), as well as profound effects on per-cell gene expression (data not shown). C. Flow cytometric analysis and PMA/ionomycin stimulation confirmed increased T cell infiltration of the MSG with an emphasis on increased activated CD8IFNg-hi,CD107a+ T cell in SjD but not CD4 T cell populations.
Figure 1. scRNAseq and spatial transcriptomics were used to understand compositional and transcriptional alterations in SG and PBMC from SjD and nonSjD. A. UMAP and leiden clustering of ~450k cells from 29 MSG and 15 paired PBMC. B. SjD exhibits loss of secretory cells and increased in inflammatory cells (adj. q-val. * < 0.05, ** < 0.01), as well as profound effects on per-cell gene expression (data not shown). C. Flow cytometric analysis and PMA/ionomycin stimulation confirmed increased T cell infiltration of the MSG with an emphasis on increased activated CD8IFNg-hi,CD107a+ T cell in SjD but not CD4 T cell populations.  Figure 2. stRNAseq revealed altered tissue organization at the transcriptional, cell:cell, and transcriptional level. A. Cell2location was used to infer the cellularity of spatially-resolved spots. B. Leiden clustering of spots reveals shifts in SjD (orange dotted box). Co-occurrence and neighborhood analysis reveals not only changes in cellularity and transcriptome, but that higher-order arrangement and the signaling neighborhoods of the gland are profoundly affected and emphasizes the most disease specific co-occurring cell types in SjD.
Figure 2. stRNAseq revealed altered tissue organization at the transcriptional, cell:cell, and transcriptional level. A. Cell2location was used to infer the cellularity of spatially-resolved spots. B. Leiden clustering of spots reveals shifts in SjD (orange dotted box). Co-occurrence and neighborhood analysis reveals not only changes in cellularity and transcriptome, but that higher-order arrangement and the signaling neighborhoods of the gland are profoundly affected and emphasizes the most disease specific co-occurring cell types in SjD. Disclosures: B. Warner, Pfizer, Astellas Bio; T. Pranzatelli, None; P. Perez, None; D. Martin, None; S. Jang, None; K. Dominick, None; E. Yamada, None; K. Byrd, None; Q. Easter, None; A. Farris, Janssen; C. Lessard, Janssen; A. Oliver, None; R. Bartolome-Casado, None; Z. Khavandgar, None; S. Gupta, None; S. Teichmann, None; A. Baer, None; J. Chiorini, None.

