Other
219 - Barriers to Dental Care for Collier County Head Start Children

Juliana G. Fitzgerald, DDS
Pediatric Dental Resident
University of Florida —Gainesville and Naples, Naples, FL
University of Florida
NAPLES, Florida, United States- MD
Maria Davila Gonzalez, DDS, MPH, DrPH
University of Florida
- KM
Kelly Magher, DMD
University of Florida —Gainesville and Naples, Naples, FL
Naples, Florida, United States - KM
Kelly Magher, DMD
University of Florida —Gainesville and Naples, Naples, FL
Naples, Florida, United States - AA
Abimbola O. Adewumi, DDS
Program Director
Florida
Gainesville, Florida, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Research Mentor(s)
Program Director(s)
Barriers to Dental Care for Collier County Head Start Children, Fitzgerald, J, Davila, M, Gorman, S, Magher, K (University of Florida, Gainesville, FL)
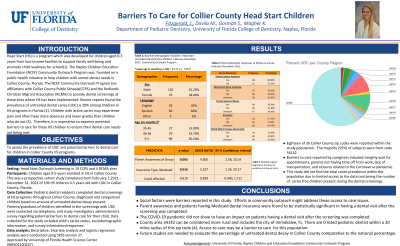
Purpose: The prevalence of untreated dental caries (UDC) is 20% among children in Head Start (HS) programs in Florida. Children with active caries may experience pain and often have more absences and lower grades than children who do not. The purpose of this study was to assess the prevalence of UDC and potential barriers to dental care for children in Collier County HS programs.
Methods: This was a prospective cohort study of 196 HS children 0-5 years old with UDC in Collier County, Florida. Pediatric dental residents completed dental screenings at HS programs throughout Collier County. Parents/guardians of children identified in the screenings with UDC were contacted via telephone, and study investigators administered a survey regarding potential barriers to dental care for their child. Data collected for the study included child’s caries status, sociodemographic information, and survey information/responses.
Results: Preliminary data analysis of the 196 subjects demonstrated the majority (60%) were male, and 69% were able to be contacted within 3 phone call attempts. Urgent dental needs (pain or clinical sign of infection) were present in 15% of subjects. Eighteen of 26 Collier County zip codes were reported within the study population. The majority (59%) of subjects were from code 34142. Barriers to care reported by caregivers included: lengthy wait for appointments, parents not having time off from work, lack of transportation, and closures related to the Coronavirus pandemic.
Conclusions: Social factors were barriers reported in this study. Efforts in community outreach might address these access to care issues.

.png)