Oral Pathology
316 - An Illustrative Case of Pediatric Peripheral Ossifying Fibroma

Sheila Fils-Aime, DDS
Resident
Jamaica Hospital Medical Center
Jamaica Hospital Medical center, New Jersey, United States- AM
Ashvi Mittal, DMD
Resident
Jamaica Hospital Medical Center
Jamaica Hospital Medical Center
Forest Hills, New York, United States - KC
Kelly Cervellione, MA, MPHIL
Jamaica Hospital Medical Center
- JW
Jeannine Weiss, DDS
Faculty
Jamaica Hospital Medical Center
Jamaica, New York, United States - JW
Jeannine Weiss, DDS
Faculty
Jamaica Hospital Medical Center
Jamaica, New York, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Program Director(s)
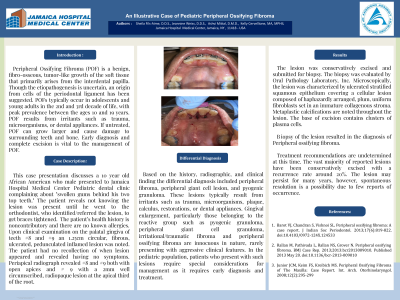
Peripheral Ossifying Fibroma (POF) is a benign, fibro-osseous, tumor-like growth of the soft tissue that primarily arises from the interdental papilla. POFs typically occur in adolescents and young adults, resulting from irritants such as trauma, microorganisms, or dental appliances. We report a 10-year-old male in active orthodontic treatment who exhibited a painless, abnormally large gingival growth behind his maxillary incisors. A 1.25 cm circular, fibrous, ulcerated, pedunculated lesion was noted on the palatal gingiva of teeth #8 and #9. Radiographic, clinical findings, and history of the present illness led to the differential diagnosis of peripheral fibroma, peripheral giant cell lesion, or pyogenic granuloma. The lesion was excised and POF was identified. No recurrence has been reported at 4 months. If untreated, POF can grow larger and cause damage to surrounding teeth and bone. Early diagnosis and complete excision is vital to the management of POF.

.png)